A network meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy and safety of adjuvant therapy after nephrectomy in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38454397
- PMCID: PMC10921661
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-024-01441-8
A network meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy and safety of adjuvant therapy after nephrectomy in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: In the past few years, there has been a continuous rise in the occurrence of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), with RCC recurrence becoming the primary factor behind fatalities. Despite numerous clinical trials, the impact of different medications on the long-term survival of patients with RCC after surgery remains uncertain. This network meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the impact of various medications on the survival and safety of drugs in individuals with RCC following nephrectomy.
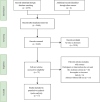
Methods: We conducted a thorough search in various databases, including CNKI, WAN FANG DATA, VIP, Web of Science, Cochrane Library (CENTRAL), PubMed, Scopus, and Embase, for articles published prior to June 2, 2023. This meta-analysis incorporated randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
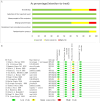
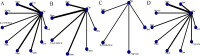
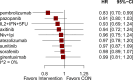
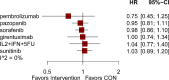
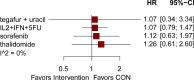
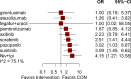
Results: The analysis included 17 studies with 14,298 participants. The findings from the disease-free survival (DFS) analysis indicated that pembrolizumab demonstrated efficacy in enhancing DFS among patients with RCC following nephrectomy when compared to the placebo group (HR = 0.83, 95%CI 0.70 to 0.99). None of the drugs included in the study significantly improved overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) after nephrectomy. For adverse events (AEs), sorafenib, pazopanib, sunitinib, and nivolumab plus ipilimumab interventions showed a higher incidence of adverse events compared with placebo.
Conclusion: The network meta-analysis yielded strong evidence indicating that pembrolizumab could potentially enhance DFS in patients with RCC following nephrectomy, surpassing the effectiveness of a placebo.
Keywords: Adjuvant therapy; Efficacy; Network meta-analysis; Renal cell carcinoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy Assessment of Post-nephrectomy Adjuvant Therapies in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2024 Jun;31(6):3894-3905. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15121-2. Epub 2024 Mar 17. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38494564
-
Adjuvant Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-targeted Therapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis.Eur Urol. 2018 Nov;74(5):611-620. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 18. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29784193 Free PMC article.
-
Pembrolizumab outperforms tyrosine kinase inhibitors as adjuvant treatment in patients with high-risk renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy.Eur Urol Oncol. 2022 Feb;5(1):120-124. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2021.12.007. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Eur Urol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34992006
-
Adjuvant Sunitinib for High-risk Renal Cell Carcinoma After Nephrectomy: Subgroup Analyses and Updated Overall Survival Results.Eur Urol. 2018 Jan;73(1):62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.09.008. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 28967554 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Efficacy of Adjuvant Targeted Therapy in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Mar 29;2022:7341294. doi: 10.1155/2022/7341294. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9861537. doi: 10.1155/2023/9861537. PMID: 35392587 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Do patients with intermediate-risk renal carcinoma who receive adjuvant pembrolizumab really benefit in recurrence-free survival? Analysis of a cohort of nephrectomies over 10 years.World J Urol. 2025 May 16;43(1):307. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05599-0. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40377723
-
Long-term outcomes and survival rates of renal cell carcinoma patients in Erbil, Iraq: a follow-up study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 3;25(1):384. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13040-9. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40033222 Free PMC article.
-
Crebanine Induces Cell Death and Alters the Mitotic Process in Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 18;26(14):6896. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146896. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725144 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Importance of Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK)-Src and Paxillin Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cureus. 2024 Jun 19;16(6):e62706. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62706. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39036223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haas NB, Manola J, Uzzo RG, Flaherty KT, Wood CG, Kane C, Jewett M, Dutcher JP, Atkins MB, Pins M, et al. Adjuvant sunitinib or sorafenib for high-risk, non-metastatic renal-cell carcinoma (ECOG-ACRIN E2805): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10032):2008–16. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00559-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

