Periodontal ligament stem cell-derived exosome-loaded Emodin mediated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy against cariogenic bacteria
- PMID: 38454402
- PMCID: PMC10919019
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04062-7
Periodontal ligament stem cell-derived exosome-loaded Emodin mediated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy against cariogenic bacteria
Abstract
Background: This study was conducted to investigate the efficiency of periodontal ligament (PDL) stem cell-derived exosome-loaded Emodin (Emo@PDL-Exo) in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) on Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus as the cariogenic bacteria.
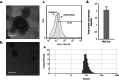
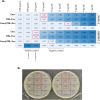
Materials and methods: After isolating and characterizing PDL-Exo, the study proceeded to prepare and verify the presence of Emo@PDL-Exo. The antimicrobial effect, anti-biofilm activity, and anti-metabolic potency of Emo, PDL-Exo, and Emo@PDL-Exo were then evaluated with and without irradiation of blue laser at a wavelength of 405 ± 10 nm with an output intensity of 150 mW/cm2 for a duration of 60 s. In addition, the study assessed the binding affinity of Emodin with GtfB and SlpA proteins using in silico molecular docking. Eventually, the study examined the generation of endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS) and changes in the gene expression levels of gelE and sprE.
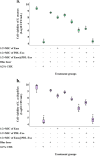
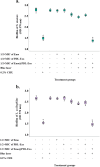
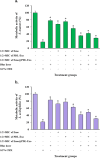
Results: The study found that using Emo@PDL-Exo-mediated aPDT resulted in a significant decrease in L. acidophilus and S. mutans by 4.90 ± 0.36 and 5.07 log10 CFU/mL, respectively (P < 0.05). The study found that using Emo@PDL-Exo for aPDT significantly reduced L. acidophilus and S. mutans biofilms by 44.7% and 50.4%, respectively, compared to untreated biofilms in the control group (P < 0.05). Additionally, the metabolic activity of L. acidophilus and S. mutans decreased by 58.3% and 71.2%, respectively (P < 0.05). The molecular docking analysis showed strong binding affinities of Emodin with SlpA and GtfB proteins, with docking scores of -7.4 and -8.2 kcal/mol, respectively. The study also found that the aPDT using Emo@PDL-Exo group resulted in the most significant reduction in gene expression of slpA and gtfB, with a decrease of 4.2- and 5.6-folds, respectively, compared to the control group (P < 0.05), likely due to the increased generation of endogenous ROS.
Discussion: The study showed that aPDT using Emo@PDL-Exo can effectively reduce the cell viability, biofilm activity, and metabolic potency of S. mutans and L. acidophilus. aPDT also significantly reduced the expression levels of gtfB and slpA mRNA due to the increased endogenous ROS generation. The findings suggest that Emo@PDL-Exo-mediated aPDT could be a promising antimicrobial approach against cariogenic microorganisms.
Keywords: Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy; Bioinformatics tools; Emodin; Exosome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Cogulu D, Saglam C. Genetic aspects of dental caries. Frontiers in Dental Medicine. 2022;3:1060177. doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2022.1060177. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

