Efficacy of acupuncture as an adjunctive treatment to patients with stable COPD: a multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled trial protocol
- PMID: 38454410
- PMCID: PMC10918953
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-024-04412-6
Efficacy of acupuncture as an adjunctive treatment to patients with stable COPD: a multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled trial protocol
Abstract
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common respiratory disease and the third leading cause of death worldwide. Previous evidence has shown that acupuncture may be an effective complementary alternative therapy for stable COPD. However, large-sample, rigorously designed long-term follow-up studies still need to be completed. Notably, the relationship between the frequency of acupuncture and clinical efficacy in studies on acupuncture for stable COPD still needs further validation. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of acupuncture for stable COPD and further investigate the dose-effect relationship of acupuncture.
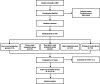
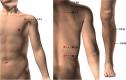
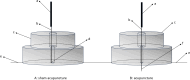
Methods/design: This is a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial that uses central randomization to randomly allocate 550 participants in a 1:1:1:1:1 ratio to once a week acupuncture group, twice a week acupuncture group, three times a week acupuncture group, sham acupuncture group and waiting-list control group. The sham acupuncture group will receive placebo acupuncture treatments three times per week, and the waiting-list control group will not receive any form of acupuncture intervention. The study consists of a 2-week baseline, 12-week of treatment, and 52-week of follow-up. Patients with COPD between 40 to 80 years old who have received stable Western medication within the previous 3 months and have had at least 1 moderate or severe acute exacerbation within the past 1 year will be included in the study. Basic treatment will remain the same for all participants. The primary outcome is the proportion of responders at week 12. Secondary outcomes include the proportion of responders at week 64, change in the St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) Scale, change in the Modified-Medical Research Council (mMRC) Scale, change in the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) Scale, change in the Lung Function Screening Indicators (LFSI), change in the 6-min walk distance (6-MWD), change in Short-Form 36 Health Survey (SF-36) Scale, the number of moderate and severe acute exacerbations and adverse event rate during the follow-up period.
Discussion: This study will provide robust evidence on whether acupuncture is safe and effective for treating stable COPD. Meanwhile, comparing the differences in efficacy between different acupuncture frequencies will further promote the optimization of acupuncture for stable COPD.
Trial registration: This study was registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2200058757), on April 16, 2022.
Keywords: Acupuncture; COPD; Protocol; Randomized controlled trial.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acupuncture improves the symptoms, gut microbiota, metabolomics, and inflammation of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled trial protocol.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 3;12:1511275. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1511275. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40098933 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of combining acupuncture with exercise training on relieving dyspnea and improving exercise tolerance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: a protocol for a single-blind, randomized, sham-controlled trial.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Sep;11(9):2968-2979. doi: 10.21037/apm-22-949. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 36217626
-
Exploration of quantitative-effectiveness association between acupuncture temporal parameters and stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2024 Jun;82:103048. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2024.103048. Epub 2024 May 10. Complement Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38734186
-
Once daily long-acting beta2-agonists and long-acting muscarinic antagonists in a combined inhaler versus placebo for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 6;3(3):CD012930. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012930.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30839102 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized controlled trial for the effect of Modified Shenling Baizhu Powder on delaying the illness progress of COPD stable phase patients (GOLD 1-2 stages): A study protocol.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 23;99(43):e22700. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022700. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33120762 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture Modulates Spatiotemporal Neuronal Dynamics in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Protocol for Simultaneous EEG-fMRI Study.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 May 7;18:2523-2539. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S516654. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40357255 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYYCXTD-D-202003/National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous