Enhancing cardiometabolic health: unveiling the synergistic effects of high-intensity interval training with spirulina supplementation on selected adipokines, insulin resistance, and anthropometric indices in obese males
- PMID: 38454429
- PMCID: PMC10921712
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-024-00785-0
Enhancing cardiometabolic health: unveiling the synergistic effects of high-intensity interval training with spirulina supplementation on selected adipokines, insulin resistance, and anthropometric indices in obese males
Abstract
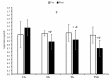
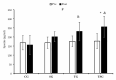
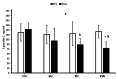
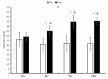
This study investigated the combined effects of 12 weeks of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and spirulina supplementation on adipokine levels, insulin resistance, anthropometric indices, and cardiorespiratory fitness in 44 obese males (aged 25-40 years). The participants were randomly assigned to one of four groups: control (CG), supplement (SG), training (TG), or training plus supplement (TSG). The intervention involved daily administration of either spirulina or a placebo and HIIT three times a week for the training groups. Anthropometric indices, HOMA-IR, VO2peak, and circulating adipokines (asprosin and lipocalin2, omentin-1, irisin, and spexin) were measured before and after the 12-week intervention. Post-intervention analysis indicated differences between the CG and the three interventional groups for body weight, fat-free mass (FFM), percent body fat (%BF), HOMA-IR, and adipokine levels (p < 0.05). TG and SG participants had increased VO2peak (p < 0.05). Spirulina supplementation with HIIT increased VO2peak, omentin-1, irisin, and spexin, while causing decreases in lipocalin-2 and asprosin levels and improvements in body composition (weight, %fat), BMI, and HOMA-IR. Notably, the combination of spirulina and HIIT produced more significant changes in circulating adipokines and cardiometabolic health in obese males compared to either supplementation or HIIT alone (p < 0.05). These findings highlight the synergistic benefits of combining spirulina supplementation with HIIT, showcasing their potential in improving various health parameters and addressing obesity-related concerns in a comprehensive manner.
Keywords: Adipokines; High-intensity interval training; Obesity; Spirulina.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of a 12-week High-Intensity Interval Training With Spirulina Supplementation on Insulin Resistance-Mediated by Apo-A, -B, and -J in Men With Obesity HIIT With Spirulina on Apolipoproteins.Eur J Sport Sci. 2025 Apr;25(4):e12285. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12285. Eur J Sport Sci. 2025. PMID: 40123054 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Spirulina Supplementation with High-Intensity Interval Training Decreases Adipokines Levels and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Men with Obesity.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 23;15(23):4891. doi: 10.3390/nu15234891. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38068748 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation with spinach-derived thylakoid augments the benefits of high intensity training on adipokines, insulin resistance and lipid profiles in males with obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 28;14:1141796. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1141796. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37576981 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of High-Intensity Interval Training and Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training for Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Childhood Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Physiol. 2020 Apr 3;11:214. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00214. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32308627 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Low-Volume High-Intensity Interval Training on Body Composition and Cardiorespiratory Fitness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2019 Nov;49(11):1687-1721. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01167-w. Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 31401727
Cited by
-
Effects of spirulina supplementation alone or with exercise on cardiometabolic health in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 27;12:1624982. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1624982. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40655486 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a 12-week High-Intensity Interval Training With Spirulina Supplementation on Insulin Resistance-Mediated by Apo-A, -B, and -J in Men With Obesity HIIT With Spirulina on Apolipoproteins.Eur J Sport Sci. 2025 Apr;25(4):e12285. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12285. Eur J Sport Sci. 2025. PMID: 40123054 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of a Dietary Microalgae (Arthrospira platensis) Supplement on Stress, Well-Being, and Performance in Water Polo Players: A Clinical Case Series.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 25;16(15):2421. doi: 10.3390/nu16152421. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oliveira JS, Pinheiro MB, Fairhall N, Walsh S, Franks TC, Kwok W, et al. Evidence on physical activity and the prevention of frailty and sarcopenia among older people: a systematic review to inform the World Health Organization physical activity guidelines. J Phys Activity Health. 2020;17(12):1247–58. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2020-0323. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kong Z, Fan X, Sun S, Song L, Shi Q, Nie J. Comparison of high-intensity interval training and moderate-to-vigorous continuous training for cardiometabolic health and exercise enjoyment in obese young women: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(7):e0158589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158589. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Delfan M, Vahed A, Bishop DJ, Amadeh Juybari R, Laher I, Saeidi A, et al. Effects of two workload-matched high intensity interval training protocols on regulatory factors associated with mitochondrial biogenesis in the soleus muscle of diabetic rats. Front Physiol. 2022;13:927969. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.927969. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

