Inhibition of OGFOD1 by FG4592 confers neuroprotection by activating unfolded protein response and autophagy after ischemic stroke
- PMID: 38454480
- PMCID: PMC10921652
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-04993-3
Inhibition of OGFOD1 by FG4592 confers neuroprotection by activating unfolded protein response and autophagy after ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background: Acute ischemic stroke is a common neurological disease with a significant financial burden but lacks effective drugs. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) and prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs) participate in the pathophysiological process of ischemia. However, whether FG4592, the first clinically approved PHDs inhibitor, can alleviate ischemic brain injury remains unclear.
Methods: The infarct volumes and behaviour tests were first analyzed in mice after ischemic stroke with systemic administration of FG4592. The knockdown of HIF-1α and pretreatments of HIF-1/2α inhibitors were then used to verify whether the neuroprotection of FG4592 is HIF-dependent. The targets predicting and molecular docking methods were applied to find other targets of FG4592. Molecular, cell biological and gene knockdown methods were finally conducted to explore the potential neuroprotective mechanisms of FG4592.
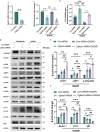
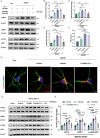
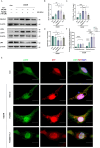
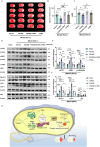
Results: We found that the systemic administration of FG4592 decreased infarct volume and improved neurological defects of mice after transient or permanent ischemia. Meanwhile, FG4592 also activated autophagy and inhibited apoptosis in peri-infarct tissue of mice brains. However, in vitro and in vivo results suggested that the neuroprotection of FG4592 was not classical HIF-dependent. 2-oxoglutarate and iron-dependent oxygenase domain-containing protein 1 (OGFOD1) was found to be a novel target of FG4592 and regulated the Pro-62 hydroxylation in the small ribosomal protein s23 (Rps23) with the help of target predicting and molecular docking methods. Subsequently, the knockdown of OGFOD1 protected the cell against ischemia/reperfusion injury and activated unfolded protein response (UPR) and autophagy. Moreover, FG4592 was also found to activate UPR and autophagic flux in HIF-1α independent manner. Blocking UPR attenuated the neuroprotection, pro-autophagy effect and anti-apoptosis ability of FG4592.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that FG4592 could be a candidate drug for treating ischemic stroke. The neuroprotection of FG4592 might be mediated by inhibiting alternative target OGFOD1, which activated the UPR and autophagy and inhibited apoptosis after ischemic injury. The inhibition of OGFOD1 is a novel therapy for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Autophagy; FG4592; Ischemic stroke; OGFOD1; Unfolded protein response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Wang YJ, Li ZX, Gu HQ, Zhai Y, Zhou Q, Jiang Y, et al. China Stroke Statistics: an update on the 2019 report from the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Institute for Global Neuroscience and Stroke Collaborations. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2022;7(5):415–450. doi: 10.1136/svn-2021-001374. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ralph GS, Parham S, Lee SR, Beard GL, Craigon MH, Ward N, et al. Identification of potential stroke targets by lentiviral vector mediated overexpression of HIF-1 alpha and HIF-2 alpha in a primary neuronal model of hypoxia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24(2):245–258. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000110532.48786.46. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

