Impact of slice thickness on reproducibility of CT radiomic features of lung tumors
- PMID: 38454921
- PMCID: PMC10918310
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.141148.2
Impact of slice thickness on reproducibility of CT radiomic features of lung tumors
Abstract
Background: Radiomics posits that quantified characteristics from radiographic images reflect underlying pathophysiology. Lung cancer (LC) is one of the prevalent forms of cancer, causing mortality. Slice thickness (ST) of computed tomography (CT) images is a crucial factor influencing the generalizability of radiomic features (RF) in oncology. There is scarcity of research that how ST affects variability of RF in LC. The present study helps in identifying the specific RF categories affected by variations in ST and provides valuable insights for researchers and clinicians working with RF in the field of LC.Hence, aim of the study is to evaluate influence of ST on reproducibility of CT-RF for lung tumors.
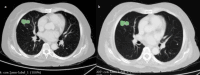
Methods: This is a prospective study, 32 patients with confirmed histopathological diagnosis of lung tumors were included. Contrast Enhanced CT (CECT) thorax was performed using a 128- Incisive CT (Philips Health Care). The image acquisition was performed with 5-mm and 2 mm STwas reconstructed retrospectively. RF were extracted from the CECT thorax images of both ST. We conducted a paired t-test to evaluate the disparity in RF between the two thicknesses. Lin's Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) was performed to identify the reproducibility of RF between the two thicknesses.
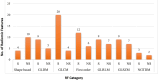
Results: Out of 107 RF, 66 (61.6%) exhibited a statistically significant distinction (p<0.05) when comparing two ST and while 41 (38.3%) RF did not show significant distinction (p>0.05) between the two ST measurements. 29 features (CCC ≥ 0.90) showed excellent to moderate reproducibility, and 78 features (CCC ≤ 0.90) showed poor reproducibility. Among the 7 RF categories, the shape-based features (57.1%) showed the maximum reproducibility whereas NGTDM-based features showed negligible reproducibility.
Conclusions: The ST had a notable impact on the majority of CT-RF of lung tumors. Shape based features (57.1%). First order (44.4%) features showed highest reproducibility compared to other RF categories.
Keywords: CT Parameters; Computed Tomography; Lung Cancer; Radiomics; Slice Thickness.
Copyright: © 2023 Gupta S et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reproducibility of lung nodule radiomic features: Multivariable and univariable investigations that account for interactions between CT acquisition and reconstruction parameters.Med Phys. 2021 Jun;48(6):2906-2919. doi: 10.1002/mp.14830. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33706419 Free PMC article.
-
Variability of computed tomography radiomics features of fibrosing interstitial lung disease: A test-retest study.Methods. 2021 Apr;188:98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.08.007. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Methods. 2021. PMID: 32891727
-
Deep Learning-based Image Conversion of CT Reconstruction Kernels Improves Radiomics Reproducibility for Pulmonary Nodules or Masses.Radiology. 2019 Aug;292(2):365-373. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019181960. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Radiology. 2019. PMID: 31210613
-
Feature selection methods and predictive models in CT lung cancer radiomics.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 Jan;24(1):e13869. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13869. Epub 2022 Dec 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36527376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mastering CT-based radiomic research in lung cancer: a practical guide from study design to critical appraisal.Br J Radiol. 2025 May 1;98(1169):653-668. doi: 10.1093/bjr/tqaf051. Br J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40100283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ESR Essentials: a step-by-step guide of segmentation for radiologists-practice recommendations by the European Society of Medical Imaging Informatics.Eur Radiol. 2025 May 22. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11621-1. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40402288 Review.
-
Correlation Between Radiological Changes of the Temporomandibular Joint and Upper Cervical Vertebrae in Degenerative Joint Disease: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Based Analytical Study.Cureus. 2024 Aug 22;16(8):e67518. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67518. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39310450 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning based radiomics approach for outcome prediction of meningioma - a systematic review.F1000Res. 2025 Mar 25;14:330. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.162306.1. eCollection 2025. F1000Res. 2025. PMID: 40206662 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

