Recent advances in photoelectrochemical platforms based on porous materials for environmental pollutant detection
- PMID: 38454947
- PMCID: PMC10915833
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra00503a
Recent advances in photoelectrochemical platforms based on porous materials for environmental pollutant detection
Abstract
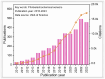
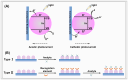
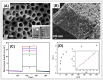
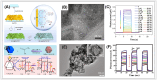
Human health and ecology are seriously threatened by harmful environmental contaminants. It is essential to develop efficient and simple methods for their detection. Environmental pollutants can be detected using photoelectrochemical (PEC) detection technologies. The key ingredient in the PEC sensing system is the photoactive material. Due to the unique characteristics, such as a large surface area, enhanced exposure of active sites, and effective mass capture and diffusion, porous materials have been regarded as ideal sensing materials for the construction of PEC sensors. Extensive efforts have been devoted to the development and modification of PEC sensors based on porous materials. However, a review of the relationship between detection performance and the structure of porous materials is still lacking. In this work, we present an overview of PEC sensors based on porous materials. A number of typical porous materials are introduced separately, and their applications in PEC detection of different types of environmental pollutants are also discussed. More importantly, special attention has been paid to how the porous material's structure affects aspects like sensitivity, selectivity, and detection limits of the associated PEC sensor. In addition, future research perspectives in the area of PEC sensors based on porous materials are presented.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


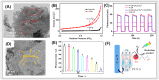
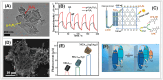
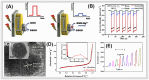
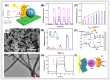



References
-
- Wang B. Wang Y. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;831:154906. - PubMed
-
- Saravanan A. Kumar P. S. Hemavathy R. V. Jeevanantham S. Harikumar P. Priyanka G. Devakirubai D. R. A. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;812:152456. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhary P. Raj A. Bharagava R. N. Chemosphere. 2018;194:229–246. - PubMed
-
- Surucu O. Mater. Today Chem. 2022;23:100639.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

