Dietary therapy of the herbal porridge improves the symptoms of functional dyspepsia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial
- PMID: 38455174
- PMCID: PMC10916651
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3911
Dietary therapy of the herbal porridge improves the symptoms of functional dyspepsia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial
Abstract
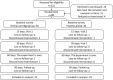
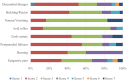
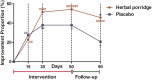
This study (ISRCTN17174559) aimed to explore the efficacy and safety of a kind of herbal porridge (Hou Gu Mi Xi) on the clinical symptoms of functional dyspepsia (FD). This was a single-center, single-dose, prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial involving 64 participants with FD (35 cases and 29 controls) for 2 months of intervention and 1 month of follow-up. The 7-point Global Overall Symptom Scale (GOSS), 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36), and other indicators were assessed at baseline (day 0), at days 15, 30, and 60 of treatment, and at follow-up 1 month after the end of the intervention. Many participants with FD achieved remission of their epigastric symptoms at follow-up on the 90th day after treatment with herbal porridge compared to the placebo group (45.71% vs. 20.69%, p = .036). Furthermore, herbal porridge appeared to be effective in improving the quality of life of participants with FD, which was reflected in the rising SF-36 scores for physical role, bodily pain, emotional role, and mental health. Although adverse events were reported, there was no overall difference in the number of adverse events between the two groups (p = .578). Herbal porridge is another effective and safe method for improving the symptoms and quality of life in patients with FD.
Keywords: dietary therapy; epigastric symptoms; functional dyspepsia; herbal porridge; randomized controlled trial; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2024 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chan, A. W. , Tetzlaff, J. M. , Altman, D. G. , Laupacis, A. , Gotzsche, P. C. , Krleza‐Jeric, K. , Hróbjartsson, A. , Mann, H. , Dickersin, K. , Berlin, J. A. , Doré, C. J. , Parulekar, W. R. , Summerskill, W. S. , Groves, T. , Schulz, K. F. , Sox, H. C. , Rockhold, F. W. , Rennie, D. , & Moher, D. (2013). SPIRIT 2013 statement: Defining standard protocol items for clinical trials. Annals of Internal Medicine, 158(3), 200–207. 10.7326/0003-4819-158-3-201302050-00583 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, X. , Nie, H. , Liu, W. , Zhou, X. , Nie, J. , Xie, B. , Chen, D. , Jiang, Y. , Zhang, K. , Fu, Y. , Yang, D. , Xiong, Y. , Zhao, Z. , Sun, X. , & Zhu, W. (2018). Efficacy and safety of Hou Gu mi xi on spleen qi deficiency in patients with nonorganic gastrointestinal disorders: Protocol for a multicenter, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Evidence‐based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2018, 1980491. 10.1155/2018/1980491 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

