Association of prognostic nutritional index with mortalities in American adult cancer survivors: A cohort study based on NHANES, 1999-2018
- PMID: 38455180
- PMCID: PMC10916647
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3877
Association of prognostic nutritional index with mortalities in American adult cancer survivors: A cohort study based on NHANES, 1999-2018
Abstract
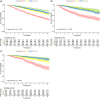
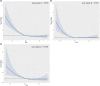
The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) has been associated with disease progression and overall survival among cancer patients. Nonetheless, the association between PNI and mortality risk in adult cancer patients within the United States remains unexplored. This study aims to elucidate the connection between PNI and prognostic outcomes in American adult cancer patients. This cohort study derived data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination database, involving 4366 American adults diagnosed with cancer between 1999 and 2018. The nutritional status was assessed using the PNI, with higher PNI scores indicating a more favorable nutritional status. The study employed Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazard regression to investigate the impact of PNI on various outcomes, including all-cause mortality (ACM), cardiovascular mortality (CAM), and malignancy tumor mortality (MTM) among adult cancer patients. Furthermore, restricted cubic spline models were used to examine the potential nonlinear relationship between the variables by creating hazard ratio (HR) curves at four specific points. The median follow-up duration was 84 months, during which 1530 (35.04%) cases of ACM occurred, including 331 (13.67%) CAM and 449 (10.45%) MTM. COX regression analysis revealed a significant inverse association between PNI and patient prognosis, with HRs of 0.95 (95% CI: 0.93-0.96, p < .001) for ACM, 0.93 (95% CI: 0.90-0.96, p < .001) for CAM, and 0.94 (95% CI: 0.91-0.97, p < .001) for MTM. Both Kaplan-Meier analyses and restricted cubic spline curves showed significant differences in mortality rates related to PNI (p < .001, nonlinear p < .001). Our study provides compelling evidence of a clear association between PNI and reduced risk of ACM, CAM, and MTM in adult cancer patients in the United States. These findings underscore the significance of incorporating PNI as a possible prognostic indicator for individuals diagnosed with cancer.
Keywords: adult; all‐cause mortality; cancer survivors; cardiovascular mortality; malignant tumor mortality; prognostic nutritional index.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic nutritional index as a predictor of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in American adults with hypertension: results from the NHANES database.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jan 6;11:1465379. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1465379. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 39834734 Free PMC article.
-
Association of prognostic nutritional index with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in adults with depression: NHANES 2005-2018.Front Nutr. 2025 May 19;12:1599830. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1599830. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40458829 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of prognostic nutritional index with cardiovascular all-cause mortality among CVD patients with diabetes or prediabetes: evidence from the NHANES 2005-2018.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 12;16:1518295. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1518295. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40013151 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic relevance of prognostic nutritional indices in gastric or gastro-esophageal junction cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1382417. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1382417. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38966640 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Prognostic Nutritional Index and Prognosis in Patients With Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 10;9:918566. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.918566. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35757355 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The association between Glycated Hemoglobin to High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and risk of cardiovascular diseases caused death among adult cancer survivors: evidence from NHANES 1999-2018.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Apr 23;24(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02566-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40264175 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Naples Prognostic Score with anemia in cancer survivors: a study based on NHANES database.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 13;15:1461962. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1461962. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40018412 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of neoadjuvant immunotherapy and lymphocyte subset predictors in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study.Cancer Med. 2024 Sep;13(17):e70228. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70228. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39275896 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and verification of prediction model for postoperative hypokalemia in patients with oral cancer.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Dec 1;42(6):778-786. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2024130. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39610075 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Association of prognostic nutritional index with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality: a nationwide population-based cohort study.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 14;12:1530452. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1530452. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40727696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deng, S. , Liu, S. , Jin, P. , Feng, S. , Tian, M. , Wei, P. , Zhu, H. , Tan, J. , Zhao, F. , & Gong, Y. (2021). Albumin reduces oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via the ERK/Nrf2/HO‐1 pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 8891373. 10.1155/2021/8891373 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eckart, A. , Struja, T. , Kutz, A. , Baumgartner, A. , Baumgartner, T. , Zurfluh, S. , Neeser, O. , Huber, A. , Stanga, Z. , Mueller, B. , & Schuetz, P. (2020). Relationship of nutritional status, inflammation, and serum albumin levels during acute illness: A prospective study. The American Journal of Medicine, 133(6), 713–722.e717. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ellez, H. I. , Keskinkilic, M. , Semiz, H. S. , Arayici, M. E. , Kısa, E. , & Oztop, I. (2023). The prognostic nutritional index (PNI): A new biomarker for determining prognosis in metastatic castration‐sensitive prostate carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5434. 10.3390/jcm12175434 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

