Technical profiles of child sexual exploitation material offenders
- PMID: 38455265
- PMCID: PMC10916919
- DOI: 10.1080/13218719.2022.2148305
Technical profiles of child sexual exploitation material offenders
Abstract
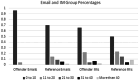
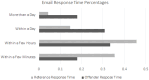
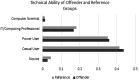
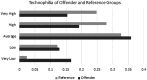
The idiographic technical profiles of child sexual exploitation material (CSEM) offenders provide insight into their behaviours and context for their interactions with technology, but minimal quantitative work has been done to evaluate their sociability, technical ability and technophilia compared to non-offenders. This work used an online survey to compare an offender group consisting of English-speaking adults previously convicted of CSEM offenses (N = 78) with a reference population of non-offenders (N = 254). The survey assessed sociability, technical ability and technophilia through self-rating and information on occupation, level of education and device ownership. The study found that CSEM offenders had slightly lower sociability than non-offenders, though not at a level of clinical interest. Additionally, CSEM offenders had no statistically significant difference in technical ability and lower overall technophilia when compared to non-offenders. This study fails to support popular perceptions of CSEM offenders being technically savvy loners who are early adopters of new technologies.
Keywords: Child pornography; child sexual exploitation material; sociability; technical profiles; technophilia.
© 2023 The Australian and New Zealand Association of Psychiatry, Psychology and Law.
Conflict of interest statement
Chad M.S. Steel has declared no conflicts of interest. Emily Newman has declared no conflicts of interest. Suzanne O’Rourke has declared no conflicts of interest. Ethel Quayle has declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self Perceptions and Cognitions of Child Sexual Exploitation Material Offenders.Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2023 Aug;67(10-11):1017-1036. doi: 10.1177/0306624X211062161. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2023. PMID: 34852672 Free PMC article.
-
Collecting and viewing behaviors of child sexual exploitation material offenders.Child Abuse Negl. 2021 Aug;118:105133. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2021.105133. Epub 2021 May 26. Child Abuse Negl. 2021. PMID: 34051488
-
Offenders convicted of child sexual exploitation material offences: characteristics of offenders and an exploration of judicial censure.Psychiatr Psychol Law. 2020 Apr 15;27(4):647-664. doi: 10.1080/13218719.2020.1742240. eCollection 2020. Psychiatr Psychol Law. 2020. PMID: 33679203 Free PMC article.
-
Child Pornography and Online Sexual Solicitation.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2020 Feb 5;22(3):10. doi: 10.1007/s11920-020-1132-y. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2020. PMID: 32025821 Review.
-
Understanding Online Child Sexual Exploitation Offenses.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2016 Aug;18(8):74. doi: 10.1007/s11920-016-0707-0. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2016. PMID: 27325170 Review.
References
-
- Armstrong, J., & Mellor, D. (2016). Internet child pornography offenders: An examination of attachment and intimacy deficits. Legal and Criminological Psychology, 21(1), 41–55. 10.1111/lcrp.12028 - DOI
-
- Babchishin, K. M., Hanson, R. K., & VanZuylen, H. (2015). Online child pornography offenders are different: A meta-analysis of the characteristics of online and offline sex offenders against children. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 44(1), 45–66. - PubMed
-
- Bryant, R. (2016). Policing digital crime. Routledge.
-
- Bursztein, E., Clarke, E., DeLaune, M., Elifff, D. M., Hsu, N., Olson, L., Shehan, J., Thakur, M., Thomas, K., & Bright, T. (2019). Rethinking the detection of child sexual abuse imagery on the internet. The World Wide Web Conference, 2601–2607. 10.1145/3308558.3313482 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources