YY1-induced lncRNA00511 promotes melanoma progression via the miR-150-5p/ADAM19 axis
- PMID: 38455406
- PMCID: PMC10915319
- DOI: 10.62347/VRBK1334
YY1-induced lncRNA00511 promotes melanoma progression via the miR-150-5p/ADAM19 axis
Abstract
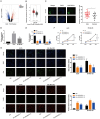
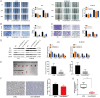
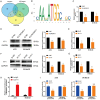
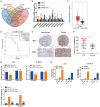
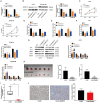
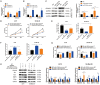
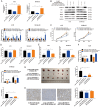
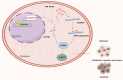
Increasing evidence indicates that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are therapeutic targets and key regulators of tumors development and progression, including melanoma. Long intergenic non-protein-coding RNA 511 (LINC00511) has been demonstrated as an oncogenic molecule in breast, stomach, colorectal, and lung cancers. However, the precise role and functional mechanisms of LINC00511 in melanoma remain unknown. This study confirmed that LINC00511 was highly expressed in melanoma cells (A375 and SK-Mel-28 cells) and tissues, knockdown of LINC00511 could inhibit melanoma cell migration and invasion, as well as the growth of subcutaneous tumor xenografts in vivo. By using Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay, it was demonstrated that the transcription factor Yin Yang 1 (YY1) is capable of binding to the LINC00511 promoter and enhancing its expression in cis. Further mechanistic investigation showed that LINC00511 was mainly enriched in the cytoplasm of melanoma cells and interacted directly with microRNA-150-5p (miR-150-5p). Consistently, the knockdown of miR-150-5p could recover the effects of LINC00511 knockdown on melanoma cells. Furthermore, ADAM metallopeptidase domain expression 19 (ADAM19) was identified as a downstream target of miR-150-5p, and overexpression of ADAM19 could promote melanoma cell proliferation. Rescue assays indicated that LINC00511 acted as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to sponge miR-150-5p and increase the expression of ADAM19, thereby activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. In summary, we identified LINC00511 as an oncogenic lncRNA in melanoma and defined the LINC00511/miR-150-5p/ADAM19 axis, which might be considered a potential therapeutic target and novel molecular mechanism the treatment of patients with melanoma.
Keywords: ADAM19; LINC00511; PI3K/AKT; ceRNA; melanoma.
AJCR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The emerging roles of LINC00511 in breast cancer development and therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 14;14:1429262. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1429262. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39206156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA LINC00511 promotes COL1A1-mediated proliferation and metastasis by sponging miR-126-5p/miR-218-5p in lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Jul 16;22(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02070-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35842617 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA NORAD regulates lung cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion by the miR-30a-5p/ADAM19 axis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 Jan 1;13(1):1-13. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32055266 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00511 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting miR-625-5p/GSPT1.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;10(12):5159-5173. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1468. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116366 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00511 Accelerates Proliferation and Invasion in Cervical Cancer Through Targeting miR-324-5p/DRAM1 Axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 12;13:10245-10256. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S255067. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33116605 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rejuvenating Hyaline Cartilage with Senescence-Targeting Si-ADAM19 Delivery for Osteoarthritis Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(13):e2414419. doi: 10.1002/advs.202414419. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39927476 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of microRNAs in bovine lymphocytes infected with Theileria annulata and treated with buparvaquone.Parasitol Res. 2024 Sep 9;123(9):318. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08341-8. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39249568
-
The emerging roles of LINC00511 in breast cancer development and therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 14;14:1429262. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1429262. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39206156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Puyana C, Denyer S, Burch T, Bhimani AD, McGuire LS, Patel AS, Mehta AI. Primary malignant melanoma of the brain: a populationbased study. World Neurosurg. 2019;130:e1091–e1097. - PubMed
-
- Rinck-Junior JA, Torricelli C, Gomez GVB, Oliveira C, Moraes AM, Lourenço GJ, Lima CSP. Influence of functional variants Asp312Asn and Lys751Gln of xeroderma pigmentosum group D (XPD) and glutathione S-transferase Mu 1 (GSTM1) and theta 1 (GSTT1) genes on cutaneous melanoma susceptibility and prognosis. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:631–635. - PubMed
-
- Huang YL, Xu Q, Wang X. Long noncoding RNA DSCAM-AS1 is associated with poor clinical prognosis and contributes to melanoma development by sponging miR-136. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:2888–2897. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
