Cytokines in Follicular Helper T Cell Biology in Physiologic and Pathologic Conditions
- PMID: 38455461
- PMCID: PMC10917579
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e8
Cytokines in Follicular Helper T Cell Biology in Physiologic and Pathologic Conditions
Abstract
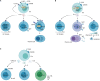
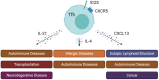
Follicular helper T cells (Tfh) play a crucial role in generating high-affinity antibodies (Abs) and establishing immunological memory. Cytokines, among other functional molecules produced by Tfh, are central to germinal center (GC) reactions. This review focuses on the role of cytokines, including IL-21 and IL-4, in regulating B cell responses within the GC, such as differentiation, affinity maturation, and plasma cell development. Additionally, this review explores the impact of other cytokines like CXCL13, IL-10, IL-9, and IL-2 on GC responses and their potential involvement in autoimmune diseases, allergies, and cancer. This review highlights contributions of Tfh-derived cytokines to both protective immunity and immunopathology across a spectrum of diseases. A deeper understanding of Tfh cytokine biology holds promise for insights into biomedical conditions.
Keywords: B cell; Cytokine; Follicular helper T cell; Germinal center; Plasma cell.
Copyright © 2024. The Korean Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into the role of follicular helper T cells in autoimmunity.Immune Netw. 2014 Feb;14(1):21-9. doi: 10.4110/in.2014.14.1.21. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Immune Netw. 2014. PMID: 24605077 Free PMC article.
-
Early T Follicular Helper Cell Responses and Germinal Center Reactions Are Associated with Viremia Control in Immunized Rhesus Macaques.J Virol. 2019 Feb 5;93(4):e01687-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01687-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30463978 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial roles of interleukin-7 in the development of T follicular helper cells and in the induction of humoral immunity.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):8998-9009. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00534-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899182 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TRAFs in Signaling Pathways Controlling T Follicular Helper Cell Differentiation and T Cell-Dependent Antibody Responses.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 22;9:2412. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02412. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30405612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Transcription Factors and Functional Roles of Follicular Helper T Cells in Human Autoimmune Diseases.Iran J Immunol. 2022 Jun;19(2):121-138. doi: 10.22034/iji.2022.92653.2164. Iran J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35767886 Review.
Cited by
-
Extended analysis on peripheral blood cytokines correlated with hepatitis B virus viral load in chronically infected patients - a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 31;11:1429926. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1429926. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39149606 Free PMC article.
-
Unsupervised Clustering of Cell Populations in Germinal Centers Using Multiplexed Immunofluorescence.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 11;14(5):530. doi: 10.3390/biology14050530. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427719 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular determinants mediating the dysregulated germinal center immune dynamics in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 13;16:1530327. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1530327. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40070830 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic history and responses to immunotherapy in individuals with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 25;15:1486583. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1486583. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40248207 Free PMC article.
-
T cell-B cell interactions in human autoimmune diseases.Curr Opin Immunol. 2025 Apr;93:102539. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2025.102539. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Curr Opin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40020254 Review.
References
-
- Victora GD, Nussenzweig MC. Germinal centers. Annu Rev Immunol. 2022;40:413–442. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki K, Spolski R, Ettinger R, Kim HP, Wang G, Qi CF, Hwu P, Shaffer DJ, Akilesh S, Roopenian DC, et al. Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J Immunol. 2004;173:5361–5371. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

