Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors and metabolic syndrome in adults from Saudi Arabia using the logarithm of triglyceride/HDL-cholesterol ratio
- PMID: 38455599
- PMCID: PMC10915911
Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors and metabolic syndrome in adults from Saudi Arabia using the logarithm of triglyceride/HDL-cholesterol ratio
Abstract
Objective: Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death globally. Metabolic syndrome (MtS) is a risk factor that increases the likelihood of CVD. The atherogenic index (AIP), calculated as the logarithm of the ratio of triglycerides (TG) to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) cholesterol in plasma, is a valuable marker for highly atherogenic small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol particles. This study aimed to explore MtS prevalence and investigate the potential of using the AIP as a predictor for CVD risk factors in adults from the Qassim region of Saudi Arabia.
Methods: The cross-sectional study enrolled 589 participants from public hospitals in nine major cities who completed a detailed questionnaire on health, diet, and lifestyle. Anthropometric measurements and some clinical parameters were measured.
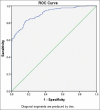
Results: The findings indicated a significant prevalence of MtS (37.5%) among participants from the Qassim Area, which was higher in males (39.9%) than females (34.9%). Nevertheless, a significant prevalence was shown for CVD risk factors among participants, with hyperglycemia (78.1%), hypertriglyceridemia (39.0%), hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia (38.9%), and hypertension (21.6%) being common. The AIP's performance in identifying CVD risk factors showed a receiver operating characteristic value of 0.909 (P < 0.001). The optimal cutoff value for the AIP was determined to be 0.468, demonstrating high sensitivity (84.8%) and specificity (78.6%).
Conclusion: Incorporating AIP into clinical practice could enhance CVD risk prediction compared to using lipid profiles alone. These findings suggest that there is a high prevalence of MtS among adults in the Qassim region of Saudi Arabia. Further longitudinal studies are needed to recommend AIP as a robust tool for predicting CVD in clinical settings.
Keywords: CVD; High-density lipoprotein; Qassim Region; metabolic syndrome; triglycerides.
Copyright: © International Journal of Health Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery calcification progression in Korean adults.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jul 2;19(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01317-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32615982 Free PMC article.
-
Anthropometrics and Plasma Atherogenic Index in Saudi Women Madinah KSA.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jan-Feb;40(3Part-II):364-370. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.3.8318. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38356847 Free PMC article.
-
Atherosclerotic Index and Traditional Anthropometry for Predicting Carotid Intima Media Thickness in Perimenopausal/Menopausal Women.J Med Assoc Thai. 2016 Oct;99 Suppl 7:S93-8. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016. PMID: 29901977
-
[AIP--atherogenic index of plasma as a significant predictor of cardiovascular risk: from research to practice].Vnitr Lek. 2006 Jan;52(1):64-71. Vnitr Lek. 2006. PMID: 16526201 Review. Czech.
-
Residual Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Focus on Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Jan-Dec;28:10742484231189597. doi: 10.1177/10742484231189597. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37641208 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between Life's Essential 8 and Atherogenic Index of Plasma in adults: insights from NHANES 2007-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 18;16:1506884. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1506884. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40041283 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the atherogenic index of plasma and long-term risk of type 2 diabetes: a 12-year cohort study based on the Japanese population.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 30;24(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02605-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39885511 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between atherogenic index of plasma and cardiovascular disease risk across Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stages 0-3: a nationwide prospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 24;24(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02593-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39856691 Free PMC article.
-
Association of atherogenic index of plasma and its modified indices with stroke risk in individuals with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stages 0-3: a longitudinal analysis based on CHARLS.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jun 14;24(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02784-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40517240 Free PMC article.
-
Association between atherogenic index of plasma with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in individuals with Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic syndrome.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Apr 26;24(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02742-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40287685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Neill S, O'Driscoll L. Metabolic syndrome:A closer look at the growing epidemic and its associated pathologies. Obes Rev. 2015;16:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome:A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention;National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute;American Heart Association;World Heart Federation;International Atherosclerosis Society;and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–5. - PubMed
-
- Bayram F, Kocer D, Gundogan K, Kaya A, Demir O, Coskun R, et al. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors in Turkish adults. J Clin Lipidol. 2014;8:206–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous