A Case of acute Myocardial Infarction in a Patient with Essential Thrombocythaemia Treated with Anagrelide
- PMID: 38455691
- PMCID: PMC10917403
- DOI: 10.12890/2024_004340
A Case of acute Myocardial Infarction in a Patient with Essential Thrombocythaemia Treated with Anagrelide
Abstract
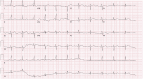
Anagrelide is a medication primarily used to manage thrombocytosis, an abnormal increase in platelet levels in the blood. It is often prescribed for patients with myeloproliferative disorders, such as essential thrombocythaemia (ET). Given the heightened susceptibility to thromboembolism associated with this condition, the primary emphasis in treatment revolves around reducing the risk of thrombotic events through the administration of cytotoxic agents. While anagrelide is generally effective in reducing platelet counts, it comes with potential side effects, including an increased risk of certain thrombotic events. Anagrelide acts by inhibiting megakaryocyte maturation and platelet release, thereby reducing platelet production. However, this platelet-lowering effect may be accompanied by an increase in platelet activation and reactivity, which could contribute to a prothrombotic state. We present a case of a 60-year-old female with a history of ET, managed with anagrelide and hydroxyurea therapy, who experienced an acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Learning points: The dual role of anagrelide: although anagrelide is effective in lowering platelet levels in essential thrombocythaemia, it can increase platelet activation, raising thrombotic risk. Clinicians need to monitor patients closely for thrombotic events.Balancing efficacy and side effects: the risk of severe side effects such as myocardial infarction, as seen in this case report, necessitates a balanced approach in using anagrelide, weighing its benefits against potential risks.
Keywords: Essential thrombocythaemia; anagrelide; myocardial infarction; thrombosis.
© EFIM 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anagrelide: a review of its use in the management of essential thrombocythaemia.Drugs. 2006;66(1):111-31. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200666010-00006. Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16398570 Review.
-
[Anagrelide in the treatment of thrombocythemia essential (ET)].Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2004 Dec;112(6):1445-50. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2004. PMID: 15962609 Polish.
-
Anagrelide: new drug. Essential thrombocythaemia: further evaluation needed for this last-resort treatment.Prescrire Int. 2006 Jun;15(83):83-6. Prescrire Int. 2006. PMID: 16764090
-
[Treatment outcome of patients with essential thrombocythemia at our department in Hungary].Orv Hetil. 2016 Feb 28;157(9):336-41. doi: 10.1556/650.2016.30323. Orv Hetil. 2016. PMID: 26895801 Hungarian.
-
Anagrelide: 20 years later.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009 Jan;9(1):37-50. doi: 10.1586/14737140.9.1.37. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19105705 Review.
References
-
- Babakhanlou R, Masarova L, Verstovsek S. A review of essential thrombocythemia and its complications. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2023;21:76–84. - PubMed
-
- Mizuta E, Takeda S, Sasaki N, Miake J, Hamada T, Shimoyama M, et al. Acute myocardial infarction in a patient with essential thrombocythemia: successful treatment with percutaneous transluminal coronary recanalization. Circ J. 2005;69:1000–1002. - PubMed
-
- Besses C, Alvarez-Larrán A. How to treat essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016;16(Suppl):S114–123. - PubMed
-
- Cervantes F. Management of essential thrombocythemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:215–221. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
