Targeting host-specific metabolic pathways-opportunities and challenges for anti-infective therapy
- PMID: 38455763
- PMCID: PMC10918472
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1338567
Targeting host-specific metabolic pathways-opportunities and challenges for anti-infective therapy
Abstract
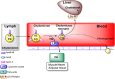
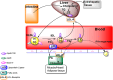
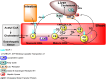
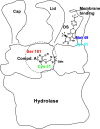
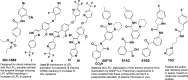
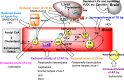
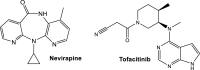
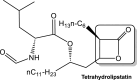
Microorganisms can takeover critical metabolic pathways in host cells to fuel their replication. This interaction provides an opportunity to target host metabolic pathways, in addition to the pathogen-specific ones, in the development of antimicrobials. Host-directed therapy (HDT) is an emerging strategy of anti-infective therapy, which targets host cell metabolism utilized by facultative and obligate intracellular pathogens for entry, replication, egress or persistence of infected host cells. This review provides an overview of the host lipid metabolism and links it to the challenges in the development of HDTs for viral and bacterial infections, where pathogens are using important for the host lipid enzymes, or producing their own analogous of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) and lipoprotein lipase (LPL) thus interfering with the human host's lipid metabolism.
Keywords: LCAT; LPL; anti-infectives; drug development; host-directed therapy; intracellular pathogens; lipid enzymes.
Copyright © 2024 Konaklieva and Plotkin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahsan L., Ossoli A. F., Freeman L. A., Vaisman B., Amar M. J., Shamburek R. D., et al. (2014). Role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase in HDL metabolism and atherosclerosis, in The HDL Handbook: biological functions and clinical implications. Komoda. T. ed. 2nd Edn. London: Academic Press, 159–194.
-
- Amar M. J. A., Sakurai T., Sakurai-Ikuta A., Sviridov D., Freeman L., Ahsan L., et al. (2015). A novel apolipoprotein C-II mimetic peptide that activates lipoprotein lipase and decreases serum triglycerides in apolipoprotein E–knockout mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 352, 227–235. 10.1124/jpet.114.220418 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

