Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing in the Case of a Concurrent Polyp and an Ectopic Tooth
- PMID: 38455780
- PMCID: PMC10918387
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.53681
Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing in the Case of a Concurrent Polyp and an Ectopic Tooth
Abstract
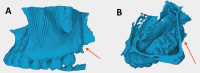
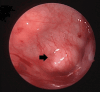
The removal of an ectopic molar tooth at the pterygomaxillary junction may be challenging. This paper presents the use of three-dimensional (3D) printing of the paranasal sinus for careful planning in a way that reduces the risk and makes surgical procedures more effective. A 26-year-old gentleman presented to the ENT department with a left antrochoanal polyp and an incidental ectopic tooth at the pterygomaxillary junction. Pre-operative 3D reconstruction of the maxillary cavity and subsequent 3D printing were used to guide the surgery and counsel the patient on potential outcomes. Left anterior functional endoscopic sinus surgery was subsequently done, and the antrochoanal polyp was completely removed. The preoperative computed tomography scan allowed for the production of the printed model to the exact size and dimensions of the ectopic molar tooth to facilitate the planning of the surgery and to aid in consenting the patient for the treatment.
Keywords: ectopic tooth; paranasal sinus diseases; polyps; transanal endoscopy; 3d printing.
Copyright © 2024, Rajendram et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- The use of 3D model planning in the management of impacted teeth. Scott J, Stagnell S, Downie I. Oral Surgery. 2018;11:125–130.
-
- Ectopic eruption of maxillary molar tooth--an unusual cause of recurrent sinusitis. Goh YH. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11358197/ Singapore Med J. 2001;42:80–81. - PubMed
-
- Dentigerous cyst associated with an ectopic tooth in the maxillary sinus: a report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Buyukkurt MC, Omezli MM, Miloglu O. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109:67–71. - PubMed
-
- A dentigerous cyst containing an ectopic canine tooth below the floor of the maxillary sinus: a case report. Dağistan S, Cakur B, Göregen M. J Oral Sci. 2007;49:249–252. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
