Nanocrystalline iron hydroxide lignocellulose filters for arsenate remediation
- PMID: 38455867
- PMCID: PMC10916386
- DOI: 10.1039/d3su00326d
Nanocrystalline iron hydroxide lignocellulose filters for arsenate remediation
Abstract
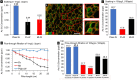
Harmful levels of environmental contaminants, such as arsenic (As), persist readily in the environment, threatening safe drinking water supplies in many parts of the world. In this paper, we present a straightforward and cost-effective filtration technology for the removal of arsenate from potable water. Biocomposite filters comprised of nanocrystalline iron oxides or oxyhydroxides mineralized within lignocellulose scaffolds constitute a promising low cost, low-tech avenue for the removal of these contaminants. Two types of iron oxide mineral phases, 2-line ferrihydrite (Fh) and magnetite (Mt), were synthesized within highly porous balsa wood using an environmentally benign modification process and studied in view of their effective removal of As from contaminated water. The mineral deposition pattern, minerology, as well as crystallinity, were assessed using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, micro-computed X-ray tomography, confocal Raman microscopy, infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray powder diffraction. Our results indicate a preferential distribution of the Fh mineral phase within the micro-porous cell wall and radial parenchyma cells of rays, while Mt is formed primarily at the cell wall/lumen interface of vessels and fibers. Water samples of known As concentrations were subjected to composite filters in batch incubation and gravity-driven flow-through adsorption tests. Eluents were analyzed using microwave plasma optical emission spectroscopy (MP-AES) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). By subjecting the filters to a flow of contaminated water, the time for As uptake was reduced to minutes rather than hours, while immobilizing the same amount of As. The retention of As within the composite filter was further confirmed through energy-dispersive X-ray mappings. Apart from addressing dangerously high levels of arsenate in potable water, these versatile iron oxide lignocellulosic filters harbor tremendous potential for addressing current and emerging environmental contaminants that are known to adsorb on iron oxide mineral phases, such as phosphate, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons or heavy metals.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phosphate competition with arsenate on poorly crystalline iron and aluminum (hydr)oxide mixtures.Chemosphere. 2020 Sep;255:126937. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126937. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 32402882
-
Perspectives on the Development of Filter Media for Point of Use Water Filters: Case Study of Arsenate Removal.Front Chem. 2022 Apr 1;10:826440. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.826440. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35433630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functionalized polymer-iron oxide hybrid nanofibers: Electrospun filtration devices for metal oxyanion removal.Water Res. 2017 Jun 15;117:207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Water Res. 2017. PMID: 28399482
-
Synthesis and characterization of nano zerovalent iron-kaolin clay (nZVI-Kaol) composite polyethersulfone (PES) membrane for the efficacious As2O3 removal from potable water samples.Chemosphere. 2022 Feb;288(Pt 1):132405. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132405. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34597639
-
Iron and aluminium based adsorption strategies for removing arsenic from water.J Environ Manage. 2011 Dec;92(12):3011-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.07.018. Epub 2011 Aug 25. J Environ Manage. 2011. PMID: 21871703 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the molecular mechanism underlying proline metabolic and catabolic pathways and some morpho-physiological traits of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) plants under arsenic stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Feb 25;25(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06262-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40000937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wei Q. Leblon B. La Rocque A. Can. J. For. Res. 2011;41:2120–2140. doi: 10.1139/x11-111. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
