Global burden of head and neck cancers from 1990 to 2019
- PMID: 38455975
- PMCID: PMC10918270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109282
Global burden of head and neck cancers from 1990 to 2019
Abstract
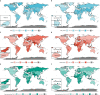
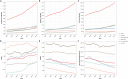
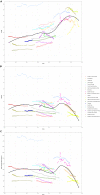
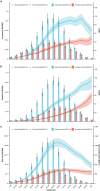
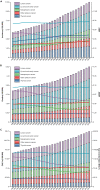
Head and neck cancer (HNC) exerts a significant healthcare burden worldwide. Insufficient data impedes a comprehensive understanding of its global impact. Through analysis of the 2019 Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database, our secondary investigation unveiled a surging global incidence of HNC, yet a decline in associated mortality and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) owing to enhanced prognosis. Particularly noteworthy is the higher incidence of escalation among females compared to males. Effective resource allocation, meticulous control of risk factors, and tailored interventions are imperative to curtail mortality rates among young individuals afflicted with HNC in underprivileged regions, as well as in elderly individuals grappling with thyroid cancer.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cancer.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

