Predicting transcription factor activity using prior biological information
- PMID: 38455978
- PMCID: PMC10918219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109124
Predicting transcription factor activity using prior biological information
Abstract
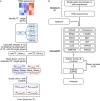
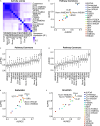
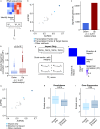
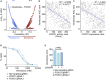
Dysregulation of normal transcription factor activity is a common driver of disease. Therefore, the detection of aberrant transcription factor activity is important to understand disease pathogenesis. We have developed Priori, a method to predict transcription factor activity from RNA sequencing data. Priori has two key advantages over existing methods. First, Priori utilizes literature-supported regulatory information to identify transcription factor-target gene relationships. It then applies linear models to determine the impact of transcription factor regulation on the expression of its target genes. Second, results from a third-party benchmarking pipeline reveals that Priori detects aberrant activity from 124 single-gene perturbation experiments with higher sensitivity and specificity than 11 other methods. We applied Priori and other top-performing methods to predict transcription factor activity from two large primary patient datasets. Our work demonstrates that Priori uniquely discovered significant determinants of survival in breast cancer and identified mediators of drug response in leukemia.
Keywords: Biocomputational method; Biological constraints; Gene network; Molecular mechanism of gene regulation.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
W.M.Y. is a former employee of Abreos Biosciences, Inc. and was compensated in part with common stock options. Pursuant to the merger and reorganization agreement between Abreos Biosciences, Inc. and Fimafeng, Inc., W.M.Y. surrendered all of his common stock options in 03/2021. T.P.B. has received research support from AstraZeneca, Blueprint Medicines as well as Gilead Sciences and is the institutional PI on the FRIDA trial sponsored by Oryzon Genomics. The authors certify that all compounds tested in this study were chosen without input from any of our industry partners. The other authors do not have competing interests, financial or otherwise.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

