The effect of personalized orthopedic insoles on plantar pressure during running in subtle cavus foot
- PMID: 38456009
- PMCID: PMC10917977
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1343001
The effect of personalized orthopedic insoles on plantar pressure during running in subtle cavus foot
Abstract
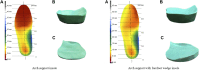
Objective: This study aims to investigate the patterns of plantar pressure distribution during running for patients with subtle cavus foot (SCF) and determine the impact of personalized orthopedic insoles with forefoot wedge on plantar pressure distribution in patients with SCF. Methods: Sixteen undergraduate participants (8 with SCF and 8 with normal arches) were recruited based on arch height index measurements. Two full-length insoles were personalized for each SCF based on plantar pressures during running, an arch support insole (ASI) and an arch support with forefoot wedge insole (AFI). Foot pressure data collected during different insole conditions in running, analyzing ten regions of footprints for peak pressure and pressure-time integral. Results: Higher peak pressures were observed in patients with SCF at the medial forefoot (p = 0.021), medial heel (p = 0.013), and lateral heel (p = 0.025), with a higher pressure-time integral also noted at the medial forefoot (p = 0.025), medial heel (p = 0.015), and lateral heel (p = 0.047) when compared to normal arches. Compared with without-insole, both the AFI and the ASI reduced peak pressure at the medial (AFI p = 0.011; ASI p = 0.024) and lateral heel (AFI p = 0.028; ASI p = 0.032). The AFI reduced peak pressure at the medial heel (p = 0.013) compared with the ASI. Both the AFI and the ASI reduced pressure-time integral at the medial forefoot (AFI p = 0.003; ASI p = 0.026), central forefoot (AFI p = 0.005; ASI p = 0.011), medial heel (AFI p = 0.017; ASI p = 0.005), and lateral heel (AFI p = 0.017; ASI p = 0.019). Additionally, the ASI reduced pressure-time integral at the big toe (p = 0.015) compared with the without-insole. Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that during running in patients with SCF, plantar pressures are concentrated in the forefoot and heel compared to the normal arch. The personalized orthotic insoles can be used to effectively redistribute plantar pressure in patients with SCF running. Incorporating a forefoot wedge to specifically address the biomechanical abnormalities associated with SCF may enhance the effectiveness of orthopedic insoles.
Keywords: Coleman block test; foot pain; forefoot valgus; heel varus; high-arched feet.
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Song and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pressure Properties of Three Different Types of Prefabricated Insoles Related to Plantar Pressure in Asymptomatic Men.Clin Orthop Surg. 2022 Dec;14(4):622-630. doi: 10.4055/cios20280. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Clin Orthop Surg. 2022. PMID: 36518933 Free PMC article.
-
Plantar pressure with and without custom insoles in patients with common foot complaints.Foot Ankle Int. 2011 Jan;32(1):57-65. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2011.0057. Foot Ankle Int. 2011. PMID: 21288435
-
An exploration of changes in plantar pressure distributions during walking with standalone and supported lateral wedge insole designs.J Foot Ankle Res. 2021 Oct 6;14(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13047-021-00493-5. J Foot Ankle Res. 2021. PMID: 34615545 Free PMC article.
-
A Study on the Effects of Lateral-Wedge Insoles on Plantar-Pressure Pattern for Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Using the Wearable Sensing Insole.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;23(1):84. doi: 10.3390/s23010084. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616681 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of orthopedic insoles on lower limb motion kinematics and kinetics in adults with flat foot: a systematic review.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 9;12:1435554. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1435554. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39070160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamin G., Anne-Laure M., Stéphane L., Marie-Lyne N. (2020). Subtle cavovarus foot: a missed risk factor for chronic foot and ankle pathologies. Int. J. Foot Ankle 4, 048. 10.23937/2643-3885/1710048 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

