Association of plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level with risk of incident dementia: a cohort study of healthy older adults
- PMID: 38456089
- PMCID: PMC10920036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100963
Association of plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level with risk of incident dementia: a cohort study of healthy older adults
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have reported associations between high plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels and risk of all-cause mortality, age-related macular degeneration, sepsis and fractures, but associations with dementia risk remain unclear. To determine whether high plasma HDL-C levels are associated with increased incident dementia risk in initially-healthy older people.
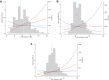
Methods: We conducted a post-hoc analysis of the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) trial; a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of daily low-dose aspirin in healthy older people. ASPREE recruited 16,703 participants aged ≥70 years (from Australia) and 2411 participants aged ≥65 years (from the US) between 2010 and 2014. Participants had no diagnosed cardiovascular disease, dementia, physical disability, or life-threatening illness at enrolment and were cognitively healthy (3MS score ≥78). All-cause dementia was a primary trial endpoint, and determined by DSM-IV criteria. Cox regression was used to examine hazard ratios between HDL-C categories <40 mg/dL, 40-60 mg/dL (reference category), 60-80 mg/dL, and >80 mg/dL and dementia. Restricted cubic spline curves were used to determine nonlinear associations. Data analysis was performed from October 2022 to January 2023.
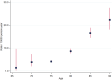
Findings: Of the 18,668 participants, 850 (4.6%) cases of incident dementia were recorded over 6.3 (SD 1.8) years. Participants with high HDL-C (>80 mg/dL) had a 27% higher risk of dementia (HR 1.27, 95% CI 1.03, 1.58). Age stratified analyses demonstrated that the risk of incident dementia was higher in participants ≥75 years compared to participants <75 years (HR 1.42, 95% CI 1.10, 1.83 vs HR 1.02, 95% CI 0.68, 1.51). Associations remained significant after adjusting for covariates including age, sex, country of enrolment, daily exercise, education, alcohol consumption, weight change over time, non-HDL-C, HDL-C-PRS, and APOE genotype.
Interpretation: In a population of initially-healthy older adults aged ≥75 years, high HDL-C levels were associated with increased risk of all-cause dementia.
Funding: National Institutes of Health, USA; National Health and Medical Research Council Australia; Monash University (Melbourne, VIC, Australia); and the Victorian Cancer Agency (Australia).
Keywords: Dementia; High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Older adults.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SMH is the recipient of National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Early Career Fellowship (APP1142198), JMCN is supported through an NHMRC Leadership Fellowship (IG 1173690). PL is supported by a National Heart Foundation Future Leader Fellowship (102604). JR is supported by an NHMRC Leadership Investigator Grant (2016438). TC is supported by an Australian Research Council Future Fellowship (FT220100294), and has received honoraria from Roche for lectures. GFW received grants from Arrowhead Pharma, Amgen, Novartis, Silence Therapeutics; consulting fee from Amgen, Novartis, Sanofi, Esperion; honoraria from Amgen, Novartis, Sanofi; support for attending meetings from Novartis, Silence Therapeutics. No other disclosures are reported by the other authors.
Figures
References
-
- Madsen C.M., Varbo A., Nordestgaard B.G. Extreme high high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is paradoxically associated with high mortality in men and women: two prospective cohort studies. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(32):2478–2486. - PubMed
-
- Colijn J.M., den Hollander A.I., Demirkan A., et al. Increased high-density lipoprotein levels associated with age-related macular degeneration: evidence from the EYE-RISK and European Eye Epidemiology Consortia. Ophthalmology. 2019;126(3):393–406. - PubMed
-
- Trinder M., Wang Y., Madsen C.M., et al. Inhibition of cholesteryl ester transfer protein preserves high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and improves survival in sepsis. Circulation. 2021;143(9):921–934. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous