Effects of Sex and Western Diet on Spatial Lipidomic Profiles for the Hippocampus, Cortex, and Corpus Callosum in Mice Using MALDI MSI
- PMID: 38456419
- PMCID: PMC11544704
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.3c00446
Effects of Sex and Western Diet on Spatial Lipidomic Profiles for the Hippocampus, Cortex, and Corpus Callosum in Mice Using MALDI MSI
Abstract
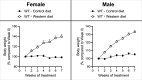
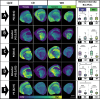
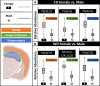
Diet is inextricably linked to human health and biological functionality. Reduced cognitive function among other health issues has been correlated with a western diet (WD) in mouse models, indicating that increases in neurodegeneration could be fueled in part by a poor diet. In this study, we use matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI MSI) to spatially map the lipidomic profiles of male and female mice that were fed a high-fat, high-sucrose WD for a period of 7 weeks. Our findings concluded that the cortex and corpus callosum showed significant lipid variation by WD in female mice, while there was little to no variation in the hippocampus, regardless of sex. On the other hand, lipid profiles were significantly affected by sex in all regions. Overall, 83 lipids were putatively identified in the mouse brain; among them, HexCer(40:1;O3) and PE(34:0) were found to have the largest statistical difference based on diet for female mice in the cortex and corpus callosum, respectively. Additional lipid changes are noted and can serve as a metric for understanding the brain's metabolomic response to changes in diet, particularly as it relates to disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MALDI-MSI reveals shared lipid signatures in sarcoid-like granulomas of mice and in a human case.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Sep 1;329(3):C768-C778. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00395.2025. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40668560
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluating sex-specific responses to western diet across the lifespan: impact on cardiac function and transcriptomic signatures in C57BL/6J mice at 530 and 640/750 days of age.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Dec 28;23(1):454. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02565-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39732652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friston K. J.; Frith C. D.; Dolan R. J.; Price C. J.; Zeki S.; Ashburner J. T.; Penny W. D.. Human Brain Function; Elsevier, 2004.
-
- Patel V.; Chisholm D.; Dua T.; Laxminarayan R.; Medina-Mora M. L.; Vos T.. Disease Control Priorities, Third ed. (Vol. 4): Mental, Neurological, and Substance Use Disorders; World Bank Publications, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Rutkowsky J. M.; Lee L. L.; Puchowicz M.; Golub M. S.; Befroy D. E.; Wilson D. W.; Anderson S.; Cline G.; Bini J.; Borkowski K.; Knotts T. A.; Rutledge J. C.; Reduced Cognitive Function, Increased Blood-Brain-Barrier Transport and Inflammatory Responses, and Altered Brain Metabolites in LDLr – /–and C57BL/6 Mice Fed a Western Diet. PLoS One 2018, 13 (2), e019190910.1371/journal.pone.0191909. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

