Study of radiomics based on dual-energy CT for nuclear grading and T-staging in renal clear cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38457546
- PMCID: PMC10919525
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037288
Study of radiomics based on dual-energy CT for nuclear grading and T-staging in renal clear cell carcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most lethal subtype of renal cell carcinoma with a high invasive potential. Radiomics has attracted much attention in predicting the preoperative T-staging and nuclear grade of ccRCC.
Objective: The objective was to evaluate the efficacy of dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) radiomics in predicting ccRCC grade and T-stage while optimizing the models.
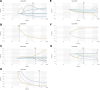
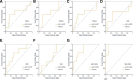
Methods: 200 ccRCC patients underwent preoperative DECT scanning and were randomized into training and validation cohorts. Radiomics models based on 70 KeV, 100 KeV, 150 KeV, iodine-based material decomposition images (IMDI), virtual noncontrasted images (VNC), mixed energy images (MEI) and MEI + IMDI were established for grading and T-staging. Receiver operating characteristic analysis and decision curve analysis (DCA) were performed. The area under the curve (AUC) values were compared using Delong test.
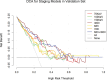
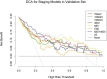
Results: For grading, the AUC values of these models ranged from 0.64 to 0.97 during training and from 0.54 to 0.72 during validation. In the validation cohort, the performance of MEI + IMDI model was optimal, with an AUC of 0.72, sensitivity of 0.71, and specificity of 0.70. The AUC value for the 70 KeV model was higher than those for the 100 KeV, 150 KeV, and MEI models. For T-staging, these models achieved AUC values of 0.83 to 1.00 in training and 0.59 to 0.82 in validation. The validation cohort demonstrated AUCs of 0.82 and 0.70, sensitivities of 0.71 and 0.71, and specificities of 0.80 and 0.60 for the MEI + IMDI and IMDI models, respectively. In terms of grading and T-staging, the MEI + IMDI model had the highest AUC in validation, with IMDI coming in second. There were statistically significant differences between the MEI + IMDI model and the 70 KeV, 100 KeV, 150 KeV, MEI, and VNC models in terms of grading (P < .05) and staging (P ≤ .001). DCA showed that both MEI + IDMI and IDMI models outperformed other models in predicting grade and stage of ccRCC.
Conclusions: DECT radiomics models were helpful in grading and T-staging of ccRCC. The combined model of MEI + IMDI achieved favorable results.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose
Figures



References
-
- Kiliçarslan G, Eroğlu Y, Kiliçarslan A. Application of different methods used to measure the apparent diffusion coefficient of renal cell carcinoma on the same lesion and its correlation with ISUP nuclear grading. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022;47:2442–52. - PubMed
-
- Delahunt B, Eble JN, Egevad L, et al. Grading of renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2019;74:4–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

