Workflow interruptions in an era of instant messaging: A detailed analysis
- PMID: 38457905
- PMCID: PMC10960569
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2024.110117
Workflow interruptions in an era of instant messaging: A detailed analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The complex practice environment and responsibilities incumbent on diagnostic radiologists creates a workflow susceptible to disruption. While interruptions have been shown to contribute to medical errors in the healthcare delivery environment, the exact impact on highly subspecialized services such as diagnostic radiology is less certain. One potential source of workflow disruption is the use of a departmental instant messaging system (Webex), to facilitate communications between radiology faculty, residents, fellows, and technologists. A retrospective review was conducted to quantify the frequency of interruption experienced by our neuroradiology fellows.
Materials and methods: Data logs were gathered comprising all instant messages sent and received within the designated group chats from July 5-December 31, 2021, during weekday shifts staffed by neuroradiology fellows. Interruptions per shift were calculated based on month, week, and day of the week.
Results: 14,424 messages were sent across 289 total shifts. The 6 fellows assigned to the main neuroradiology reading room sent 3258 messages and received 10,260 messages from technologists and other staff. There was an average of 50 interruptions per shift when examined by month (range 48-53), and 52 interruptions per shift when examined by day of the week (range 40-60).
Conclusion: Neuroradiology fellows experience frequent interruptions from the departmental instant messaging system. These disruptions, when considered in conjunction with other non-interpretative tasks, may have negative implications for workflow efficiency, requiring iterative process improvements when incorporating new technology into the practice environment of diagnostic radiology.
Keywords: Diagnostic radiology; Instant messaging; Interruptions; Workflow.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
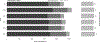
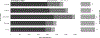
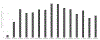
Similar articles
-
Workflow Interruptions and Effect on Study Interpretation Efficiency.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2022 Nov-Dec;51(6):848-851. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35870962
-
The radiologist's workflow environment: evaluation of disruptors and potential implications.J Am Coll Radiol. 2014 Jun;11(6):589-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2013.12.026. Epub 2014 Apr 26. J Am Coll Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24775910
-
Reducing interruptions during duty radiology shifts, assessment of its benefits and review of factors affecting the radiology working environment.Clin Radiol. 2018 Aug;73(8):759.e19-759.e25. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 May 28. Clin Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29853302
-
Real-Time Electronic Dashboard Technology and Its Use to Improve Pediatric Radiology Workflow.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2018 Jan-Feb;47(1):3-5. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 19. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28533102 Review.
-
Design of overnight radiology shifts - primum non nocere.Emerg Radiol. 2024 Jun;31(3):429-434. doi: 10.1007/s10140-024-02224-2. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Emerg Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38581613 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

