SMARCA4 is a haploinsufficient B cell lymphoma tumor suppressor that fine-tunes centrocyte cell fate decisions
- PMID: 38458188
- PMCID: PMC11003852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.02.011
SMARCA4 is a haploinsufficient B cell lymphoma tumor suppressor that fine-tunes centrocyte cell fate decisions
Abstract
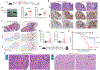
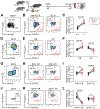
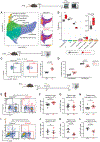
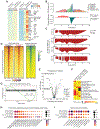
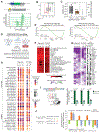
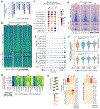
SMARCA4 encodes one of two mutually exclusive ATPase subunits in the BRG/BRM associated factor (BAF) complex that is recruited by transcription factors (TFs) to drive chromatin accessibility and transcriptional activation. SMARCA4 is among the most recurrently mutated genes in human cancer, including ∼30% of germinal center (GC)-derived Burkitt lymphomas. In mice, GC-specific Smarca4 haploinsufficiency cooperated with MYC over-expression to drive lymphomagenesis. Furthermore, monoallelic Smarca4 deletion drove GC hyperplasia with centroblast polarization via significantly increased rates of centrocyte recycling to the dark zone. Mechanistically, Smarca4 loss reduced the activity of TFs that are activated in centrocytes to drive GC-exit, including SPI1 (PU.1), IRF family, and NF-κB. Loss of activity for these factors phenocopied aberrant BCL6 activity within murine centrocytes and human Burkitt lymphoma cells. SMARCA4 therefore facilitates chromatin accessibility for TFs that shape centrocyte trajectories, and loss of fine-control of these programs biases toward centroblast cell-fate, GC hyperplasia and lymphoma.
Keywords: B-cell; BAF; SMARCA4; SWI/SNF; epigenetics; germinal center; immunology; lymphoma; transcription.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.A., advisory board for Sobi and OPNA, research funding from Genentech. A.M., research funding from Janssen, Epizyme and Daiichi Sankyo, consulting for Exo Therapeutics, Treeline Biosciences, Astra Zeneca, Epizyme. C.S., consulting for Seattle Genetics, AbbVie, and Bayer, research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Epizyme and Trillium Therapeutics Inc. C.E.M. is a cofounder and board member for Biotia and Onegevity Health, advisor or grantee for Abbvie, ArcBio, Daiichi Sankyo, DNA Genotek, Tempus Labs, and Whole Biome. M.R.G., research funding from Sanofi, Kite/Gilead, Allogene and Abbvie, honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, Abbvie and DAVA Oncology.
Figures


References
-
- Doane AS, Chu CS, Di Giammartino DC, Rivas MA, Hellmuth JC, Jiang Y, Yusufova N, Alonso A, Roeder RG, Apostolou E, et al. (2021). OCT2 pre-positioning facilitates cell fate transition and chromatin architecture changes in humoral immunity. Nature immunology 22, 1327–1340. 10.1038/s41590-021-01025-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dominguez PM, Ghamlouch H, Rosikiewicz W, Kumar P, Beguelin W, Fontan L, Rivas MA, Pawlikowska P, Armand M, Mouly E, et al. (2018). TET2 Deficiency Causes Germinal Center Hyperplasia, Impairs Plasma Cell Differentiation, and Promotes B-cell Lymphomagenesis. Cancer discovery 8, 1632–1653. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0657. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Ortega-Molina A, Geng H, Ying HY, Hatzi K, Parsa S, McNally D, Wang L, Doane AS, Agirre X, et al. (2017). CREBBP Inactivation Promotes the Development of HDAC3-Dependent Lymphomas. Cancer discovery 7, 38–53. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0975. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

