Scoping review of assessment tools for, magnitudes of and factors associated with problem drinking in population-based studies
- PMID: 38458797
- PMCID: PMC10928735
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080657
Scoping review of assessment tools for, magnitudes of and factors associated with problem drinking in population-based studies
Abstract
Background: The term "problem drinking" includes a spectrum of alcohol problems ranging from excessive or heavy drinking to alcohol use disorder. Problem drinking is a leading risk factor for death and disability globally. It has been measured and conceptualised in different ways, which has made it difficult to identify common risk factors for problem alcohol use. This scoping review aims to synthesise what is known about the assessment of problem drinking, its magnitude and associated factors.
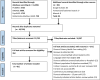
Methods: Four databases (PubMed, Embase, PsycINFO, Global Index Medicus) and Google Scholar were searched from inception to 25 November 2023. Studies were eligible if they focused on people aged 15 and above, were population-based studies reporting problem alcohol use and published in the English language. This review was reported based on guidelines from the 'Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews Checklist'. Critical appraisal was done using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale.
Results: From the 14 296 records identified, 10 749 underwent title/abstract screening, of which 352 full-text articles were assessed, and 81 articles were included for data extraction. Included studies assessed alcohol use with self-report quantity/frequency questionnaires, criteria to determine risky single occasion drinking, validated screening tools, or structured clinical and diagnostic interviews. The most widely used screening tool was the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test. Studies defined problem drinking in various ways, including excessive/heavy drinking, binge drinking, alcohol use disorder, alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence. Across studies, the prevalence of heavy drinking ranged from <1.0% to 53.0%, binge drinking from 2.7% to 48.2%, alcohol abuse from 4.0% to 19.0%, alcohol dependence from 0.1% to 39.0% and alcohol use disorder from 2.0% to 66.6%. Factors associated with problem drinking varied across studies. These included sociodemographic and economic factors (age, sex, relationship status, education, employment, income level, religion, race, location and alcohol outlet density) and clinical factors (like medical problems, mental disorders, other substance use and quality of life).
Conclusions: Due to differences in measurement, study designs and assessed risk factors, the prevalence of and factors associated with problem drinking varied widely across studies and settings. The alcohol field would benefit from harmonised measurements of alcohol use and problem drinking as this would allow for comparisons to be made across countries and for meta-analyses to be conducted.
Trial registration number: Open Science Framework ID: https://osf.io/2anj3.
Keywords: audit; epidemiologic studies; ethanol; mental health; substance misuse; systematic review.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deployment of personnel to military operations: impact on mental health and social functioning.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 1;14(1):1-127. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.6. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131363 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Recovery schools for improving behavioral and academic outcomes among students in recovery from substance use disorders: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 4;14(1):1-86. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.9. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131375 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative alcohol cessation intervention for postoperative complications.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 8;11(11):CD008343. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008343.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30408162 Free PMC article.
-
Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;17(2):e1173. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1173. eCollection 2021 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 37131927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychosocial factors behind addiction-a six-wave longitudinal comparison of at-risk gambling and drinking.Alcohol Alcohol. 2024 Nov 18;60(1):agae089. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agae089. Alcohol Alcohol. 2024. PMID: 39761683 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the journey of families navigating problem drinking in South Asia: a scoping review.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 9;25(1):1715. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22967-y. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40346530 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Alcohol Use Prior to Major Cancer Surgery: Timeline Follow Back Interview Compared to Four Other Markers.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;16(12):2261. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122261. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global status report on alcohol and health 2018. 2019.
-
- World Health Organization . Management of Substance Abuse Unit. Global status report on alcohol and health 2014. World Health Organization, 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical