The role of interdecadal climate oscillations in driving Arctic atmospheric river trends
- PMID: 38459001
- PMCID: PMC10923828
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45159-5
The role of interdecadal climate oscillations in driving Arctic atmospheric river trends
Abstract
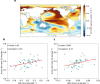
Atmospheric rivers (ARs), intrusions of warm and moist air, can effectively drive weather extremes over the Arctic and trigger subsequent impact on sea ice and climate. What controls the observed multi-decadal Arctic AR trends remains unclear. Here, using multiple sources of observations and model experiments, we find that, contrary to the uniform positive trend in climate simulations, the observed Arctic AR frequency increases by twice as much over the Atlantic sector compared to the Pacific sector in 1981-2021. This discrepancy can be reconciled by the observed positive-to-negative phase shift of Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation (IPO) and the negative-to-positive phase shift of Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), which increase and reduce Arctic ARs over the Atlantic and Pacific sectors, respectively. Removing the influence of the IPO and AMO can reduce the projection uncertainties in near-future Arctic AR trends by about 24%, which is important for constraining projection of Arctic warming and the timing of an ice-free Arctic.
© 2024. Battelle Memorial Institute, Chen, Rasch, Fu, Kravitz, Cassano, Maslowski.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Rantanen M, et al. The Arctic has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979. Commun. Earth\Environ. 2022;3:168.
-
- Wang X, Liu Y, Key JR, Dworak R. A new perspective on four decades of changes in arctic sea ice from satellite observations. Remote Sens. 2022;14:1846. doi: 10.3390/rs14081846. - DOI
-
- Årthun M, Eldevik T, Smedsrud LH, Skagseth Ø, Ingvaldsen RB. Quantifying the influence of Atlantic heat on Barents Sea ice variability and retreat. J. Clim. 2012;25:4736–4743. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00466.1. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

