Speech-induced suppression during natural dialogues
- PMID: 38459110
- PMCID: PMC10923813
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-05945-9
Speech-induced suppression during natural dialogues
Abstract
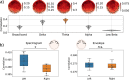
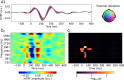
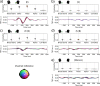
When engaged in a conversation, one receives auditory information from the other's speech but also from their own speech. However, this information is processed differently by an effect called Speech-Induced Suppression. Here, we studied brain representation of acoustic properties of speech in natural unscripted dialogues, using electroencephalography (EEG) and high-quality speech recordings from both participants. Using encoding techniques, we were able to reproduce a broad range of previous findings on listening to another's speech, and achieving even better performances when predicting EEG signal in this complex scenario. Furthermore, we found no response when listening to oneself, using different acoustic features (spectrogram, envelope, etc.) and frequency bands, evidencing a strong effect of SIS. The present work shows that this mechanism is present, and even stronger, during natural dialogues. Moreover, the methodology presented here opens the possibility of a deeper understanding of the related mechanisms in a wider range of contexts.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

