Vitamin D and risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the SUN project: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 38459212
- PMCID: PMC11368983
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-024-02324-3
Vitamin D and risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the SUN project: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Purpose: Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with multiple chronic diseases, including metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (T2D). The aim of the study was to analyze the association between validated predicted serum vitamin D status and the risk of developing T2D in a large prospective cohort based on a Mediterranean population.
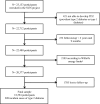
Methods: The SUN project is a prospective and dynamic Spanish cohort that gathers university graduates who have answered lifestyle questionnaires, including a validated Food Frequency Questionnaire. The association between predicted serum vitamin D and the risk of T2D was assessed through Cox regression models according to quartiles (Q) of predicted vitamin D at baseline. The models were adjusted for potential confounders and sensitivity analyses were performed to ensure the robustness of our findings.
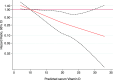
Results: Our study included a total of 18,594 participants and after a total follow-up of 238,078 person-years (median follow-up of 13.5 years), 209 individuals were diagnosed with incident T2D. We found a significant inverse association between predicted levels of serum vitamin D and the risk of developing T2D, after adjusting for potential confounders and performing different sensitivity analyses (hazard ratio Q4 vs. Q1: 0.48, 95% CI 0.26-0.88; p for trend = 0.032).
Conclusion: The outcomes suggest that higher levels of vitamin D at baseline may be associated with a reduced risk of developing T2D.
Keywords: Predicted vitamin D; Prospective cohort; SUN project; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, collection, analysis and interpretation of the data; they did not intervene either in the writing process nor the decision to publish the outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Schleicher RL, Sternberg MR, Looker AC, Yetley EA, Lacher DA, Sempos CT et al (2016) National estimates of serum total 25-hydroxyvitamin D and metabolite concentrations measured by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in the US population during 2007–2010. J Nutr 146(5):1051–1061 10.3945/jn.115.227728 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RD 06/0045/European Regional Development Fund
- PI10/02293/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PI13/00615/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PI14/01668/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PI17/01795/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PI20/00564/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PI10/02658/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PI14/01798/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PI14/01764/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- G03/140/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- 27/2011/Gobierno de Navarra
- 45/2011/Gobierno de Navarra
- 122/2014/Gobierno de Navarra
- 2020/021/Plan Nacional sobre Drogas
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

