Application of lecture-and-team-based learning in stomatology: in-class and online
- PMID: 38459478
- PMCID: PMC10924390
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-024-05235-2
Application of lecture-and-team-based learning in stomatology: in-class and online
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate stomatological students' learning efficacy and their attitude towards Lecture-Team-Based Learning (LTBL) on topics regarding the design of removable partial dentures via in-class, online, and both in combination.
Methods: Students from seven distinct grades participated in the course in their fourth academic year (Years 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, and 2021). Students of Years 2015-2019 attended in-class LTBL, students of Year 2020 attended online LTBL, and students of Year 2021 attended the combination mode. The scores of three examinations were compared, namely, individual readiness assessment test, team readiness assurance test, and individual application test. Visual Analog Scales (VAS) were used for students to self-assess their mastery of prosthodontics knowledge before and after the course. Anonymous questionnaires were delivered to evaluate their satisfaction with LTBL via a Likert scale.
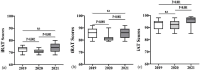
Results: In each academic year, the three exam scores were significantly improved as the course progressed and VAS-post scores were significantly higher than VAS-pre scores. The three examination and VAS scores of students in Year 2020 were significantly lower than those in Years 2019 and 2021. Students were highly satisfied with the LTBL course based on the three parameters of knowledge acquisition, teamwork, and classroom atmosphere.
Conclusion: Students were highly satisfied with the LTBL course and their learning performance was improved as the course progressed both in-class and online. Online LTBL could be adopted when students have to study online, while in-class LTBL could perform better when combined with video records of an online LTBL course.
Keywords: Chinese undergraduate; Lecture-based learning; Lecture-team-based learning; Stomatology; Team-based learning.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of team-based learning on perceived teamwork and academic performance in a health assessment subject.Collegian. 2015;22(3):299-305. doi: 10.1016/j.colegn.2014.05.001. Collegian. 2015. PMID: 26552201
-
Semi-flipped classroom-based learning interventions in a traditional curriculum of oral medicine: students' perceptions and teaching achievements.BMC Med Educ. 2023 Jan 19;23(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04017-6. BMC Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 36658530 Free PMC article.
-
The application of flipped classroom combined with team-based learning in the orthopedic clinical teaching.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 27;102(43):e35803. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035803. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37904444 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 7;19(3):e1339. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1339. eCollection 2023 Sep. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37425620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Innovative Instructional Reform and Practice of Oral Microbiology-A Course in Undergraduate Stomatology Curriculum].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Nov;52(6):939-942. doi: 10.12182/20211160303. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 34841758 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Team based learning pedagogy enhances the education quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Apr 21;25(1):580. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07175-x. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40259292 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of generative artificial intelligence-based teaching versus traditional teaching methods in medical education: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Aug 19;25(1):1175. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07750-2. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40830476 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating team-based and peer-teaching strategies for standardized dental residency: a path to active learning and professional growth.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Apr 26;25(1):618. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07023-y. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40287670 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic case-based learning model: conducive to enhancing the practical learning effectiveness of dermatology for medical students.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):957. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07474-3. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40598129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nawabi S, Javed MQ, Bilal R. Problem-based Learning and Team-based Learning as a Novel Package Approach. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2021;30(6):710–5. - PubMed
-
- Larry K, Michaelsen L, Bauman Knight A, Dee Fink L, Fink L. Team-based learning: a transformative use of small groups in College Teaching. Praeger; 2002.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

