Phenotypic, molecular detection, and Antibiotic Resistance Profile (MDR and XDR) of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Farmed Tilapia zillii and Mugil cephalus
- PMID: 38459543
- PMCID: PMC10921648
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-03942-y
Phenotypic, molecular detection, and Antibiotic Resistance Profile (MDR and XDR) of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Farmed Tilapia zillii and Mugil cephalus
Abstract
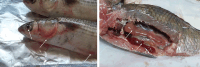
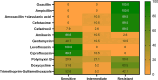
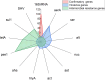
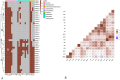
In the present study, Aeromonas hydrophila was isolated from Tilapia zillii and Mugil cephalus samples collected during different seasons from various Suez Canal areas in Egypt. The prevalence of A. hydrophila, virulence genes, and antibiotic resistance profile of the isolates to the commonly used antibiotics in aquaculture were investigated to identify multiple drug resistance (MDR) and extensive drug-resistant (XDR) strains. In addition, a pathogenicity test was conducted using A. hydrophila, which was isolated and selected based on the prevalence of virulence and resistance genes, and morbidity of natural infected fish. The results revealed that A. hydrophila was isolated from 38 of the 120 collected fish samples (31.6%) and confirmed phenotypically and biochemically. Several virulence genes were detected in retrieved A. hydrophila isolates, including aerolysin aerA (57.9%), ser (28.9%), alt (26.3%), ast (13.1%), act (7.9%), hlyA (7.9%), and nuc (18.4%). Detection of antibiotic-resistant genes revealed that all isolates were positive for blapse1 (100%), blaSHV (42.1%), tetA (60.5%), and sul1 (42.1%). 63.1% of recovered isolates were considered MDR, while 28.9% of recovered isolates were considered XDR. Some isolates harbor both virulence and MDR genes; the highest percentage carried 11, followed by isolates harboring 9 virulence and resistance genes. It could be concluded that the high prevalence of A. hydrophila in aquaculture species and their diverse antibiotic resistance and virulence genes suggest the high risk of Aeromonas infection and could have important implications for aquaculture and public health.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; Antibiotic resistance, cultured freshwater fish; Prevalence; Virulence genes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cross-sectional analysis of risk factors associated with Mugil cephalus in retail fish markets concerning methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Aeromonas hydrophila.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Feb 2;14:1348973. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1348973. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38371296 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of colistin resistance and characterization of antimicrobial resistance and virulence factors of Aeromonas hydrophila, Salmonella spp., and Vibrio cholerae isolated from hybrid red tilapia cage culture.PeerJ. 2023 Feb 23;11:e14896. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14896. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36855429 Free PMC article.
-
Virulent and Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Diseased Nile Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis niloticus) in Egypt with Sequencing of Some Virulence-Associated Genes.Biocontrol Sci. 2021;26(3):167-176. doi: 10.4265/bio.26.167. Biocontrol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34556619
-
A review on pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and their mitigation through medicinal herbs in aquaculture.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 28;9(3):e14088. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14088. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36938468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Aeromonas hydrophila infection on aquatic animals: A mini-review.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Oct 6;9:1023784. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1023784. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36277060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, Identification, and Characterisation of a Novel ST2378 Aeromonas hydrophila Strain from Naturally Diseased Frogs, Rana dybowskii.Pathogens. 2024 Jun 30;13(7):552. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13070552. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39057779 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from freshwater fishes at Middle Upper Egypt.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 18;15(1):5920. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89465-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39966501 Free PMC article.
-
Aeromonas characteristics in Iran, Southwest Asia; a systematic review and meta-analysis on epidemiology, reservoirs and antibiotic resistance profile from aquatic environments to human society during 2000-2023.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Feb 26;21(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04431-y. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40001054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Mokaddem AK, Abdel-moneam DA, Ibrahim RA, Saleh M, Shaalan M. Molecular identification, histopathological analysis and immunohistochemical characterization of non-pigmented Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. Salmonicida in Mugil Carinatus (Valenciennes, 1836) Aquacult Rep. 2022;24:101103.
-
- Sreedharan K, Philip R, Singh ISB. Virulence potential and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of motile aeromonads associated with freshwater ornamental fish culture systems: a possible threat to public health. Braz J Microbiol. 2012;43:754–65. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822012000200040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

