Uncovering the spread of drug-resistant bacteria through next-generation sequencing based surveillance: transmission of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales by a contaminated duodenoscope
- PMID: 38459544
- PMCID: PMC10924313
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-024-01386-5
Uncovering the spread of drug-resistant bacteria through next-generation sequencing based surveillance: transmission of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales by a contaminated duodenoscope
Abstract
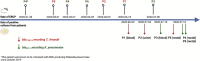
Contamination of duodenoscopes is a significant concern due to the transmission of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) among patients who undergo endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), resulting in outbreaks worldwide. In July 2020, it was determined that three different patients, all had undergone ERCP with the same duodenoscope, were infected. Two patients were infected with blaCTX-M-15 encoding Citrobacter freundii, one experiencing a bloodstream infection and the other a urinary tract infection, while another patient had a bloodstream infection caused by blaSHV-12 encoding Klebsiella pneumoniae. Molecular characterization of isolates was available as every ESBL-producing isolate undergoes Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) for comprehensive genomic analysis in our center. After withdrawing the suspected duodenoscope, we initiated comprehensive epidemiological research, encompassing case investigations, along with a thorough duodenoscope investigation. Screening of patients who had undergone ERCP with the implicated duodenoscope, as well as a selection of hospitalized patients who had ERCP with a different duodenoscope during the outbreak period, led to the discovery of three additional cases of colonization in addition to the three infections initially detected. No microorganisms were detected in eight routine culture samples retrieved from the suspected duodenoscope. Only after destructive dismantling of the duodenoscope, the forceps elevator was found to be positive for blaSHV-12 encoding K. pneumoniae which was identical to the isolates detected in three patients. This study highlights the importance of using NGS to monitor the transmission of MDROs and demonstrates that standard cultures may fail to detect contaminated medical equipment such as duodenoscopes.
Keywords: Citrobacter freundii; Klebsiella pneumoniae; CTXM-15; Contamination; Duodenoscope; Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP); Extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL); Multi locus sequence typing (MLST); Next-generation sequencing (NGS); Nosocomial transmission; SHV-12.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Fraser TG, Reiner S, Malczynski M, Yarnold PR, Warren J, Noskin GA. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa cholangitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: failure of routine endoscope cultures to prevent an outbreak. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2004;25(10):856–859. doi: 10.1086/502309. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

