A glutamine tug-of-war between cancer and immune cells: recent advances in unraveling the ongoing battle
- PMID: 38459595
- PMCID: PMC10921613
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-02994-0
A glutamine tug-of-war between cancer and immune cells: recent advances in unraveling the ongoing battle
Erratum in
-
Correction: A glutamine tug-of-war between cancer and immune cells: recent advances in unraveling the ongoing battle.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 26;43(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03018-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38532446 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
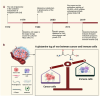
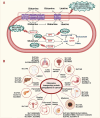
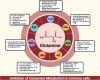
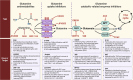
Glutamine metabolism plays a pivotal role in cancer progression, immune cell function, and the modulation of the tumor microenvironment. Dysregulated glutamine metabolism has been implicated in cancer development and immune responses, supported by mounting evidence. Cancer cells heavily rely on glutamine as a critical nutrient for survival and proliferation, while immune cells require glutamine for activation and proliferation during immune reactions. This metabolic competition creates a dynamic tug-of-war between cancer and immune cells. Targeting glutamine transporters and downstream enzymes involved in glutamine metabolism holds significant promise in enhancing anti-tumor immunity. A comprehensive understanding of the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying this interplay is crucial for developing innovative therapeutic approaches that improve anti-tumor immunity and patient outcomes. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of recent advances in unraveling the tug-of-war of glutamine metabolism between cancer and immune cells and explore potential applications of basic science discoveries in the clinical setting. Further investigations into the regulation of glutamine metabolism in cancer and immune cells are expected to yield valuable insights, paving the way for future therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Cancer; Glutamine metabolism; Immune cells; Therapeutic strategies; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81627901/National Natural Science Foundation of China-China Academy of General Technology Joint Fund for Basic Research
- 81972863/National Natural Science Foundation of China-China Academy of General Technology Joint Fund for Basic Research
- 82030082/National Natural Science Foundation of China-China Academy of General Technology Joint Fund for Basic Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

