Transcriptome and single-cell transcriptomics reveal prognostic value and potential mechanism of anoikis in skin cutaneous melanoma
- PMID: 38460046
- PMCID: PMC10924820
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-00926-0
Transcriptome and single-cell transcriptomics reveal prognostic value and potential mechanism of anoikis in skin cutaneous melanoma
Abstract
Background: Skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM) is a highly lethal cancer, ranking among the top four deadliest cancers. This underscores the urgent need for novel biomarkers for SKCM diagnosis and prognosis. Anoikis plays a vital role in cancer growth and metastasis, and this study aims to investigate its prognostic value and mechanism of action in SKCM.
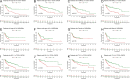
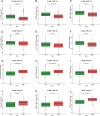
Methods: Utilizing consensus clustering, the SKCM samples were categorized into two distinct clusters A and B based on anoikis-related genes (ANRGs), with the B group exhibiting lower disease-specific survival (DSS). Gene set enrichment between distinct clusters was examined using Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis.
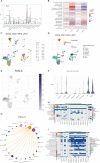
Results: We created a predictive model based on three anoikis-related differently expressed genes (DEGs), specifically, FASLG, IGF1, and PIK3R2. Moreover, the mechanism of these prognostic genes within the model was investigated at the cellular level using the single-cell sequencing dataset GSE115978. This analysis revealed that the FASLG gene was highly expressed on cluster 1 of Exhausted CD8( +) T (Tex) cells.
Conclusions: In conclusion, we have established a novel classification system for SKCM based on anoikis, which carries substantial clinical implications for SKCM patients. Notably, the elevated expression of the FASLG gene on cluster 1 of Tex cells could significantly impact SKCM prognosis through anoikis, thus offering a promising target for the development of immunotherapy for SKCM.
Keywords: Anoikis; Single-cell data analysis; Skin cutaneous melanoma; TCGA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The writers indicated that their work was not influenced by competing financial interests or personal connection.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, et al. Global cancer observatory: cancer today. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
