Pilot observational cohort study to determine whether waveform and flow traces from mechanical insufflation-exsufflation (MI-E) can be used to identify laryngeal responses to MI-E and thus optimise treatment algorithms in neuromuscular patients in a tertiary centre: a protocol description
- PMID: 38460974
- PMCID: PMC10928760
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjresp-2022-001599
Pilot observational cohort study to determine whether waveform and flow traces from mechanical insufflation-exsufflation (MI-E) can be used to identify laryngeal responses to MI-E and thus optimise treatment algorithms in neuromuscular patients in a tertiary centre: a protocol description
Abstract
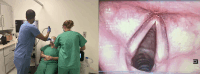
Introduction: Patients with neuromuscular disease often have a weak and ineffective cough due to respiratory muscle weakness. One treatment option is mechanical insufflation-exsufflation (MI-E), also known as cough assist, which is known to increase cough strength. However, some patients have a laryngeal response to MI-E, which can make the treatment ineffective. Currently, the only method for assessing this is via nasal endoscopy while using MI-E. Some MI-E devices have onboard secure data (SD) cards, which allow the visualisation of waveforms. We hypothesise that the waveforms can be used to identify laryngeal responses to the MI-E.
Methods and analysis: Participants will complete baseline assessments of spirometry, peak cough flow and sniff nasal inspiratory pressure. A nasal endoscope will be used to visualise the larynx during simultaneous MI-E via a mask with a drilled hole. MI-E will be delivered by an experienced physiotherapist. Four cycles of MI-E at a range of prescriptions will be delivered. MI-E waveforms will be downloaded into Care Orchestrator Essence software (Philips, Murraysville). Data will be collected prospectively and reviewed in a descriptive context, providing trends and potential rationales describing the waveforms in comparison to the nasal endoscope videos.
Ethics and dissemination: This protocol has been reviewed by the East of England-Cambridge Central Research Ethics Committee, who have granted a favourable ethical opinion. The study opened to recruitment in January 2022 and aims to publish trial results in June 2024.
Trial registration number: NCT05189600.
Keywords: Cough/Mechanisms/Pharmacology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SKM: consultancy for Philips Respironics, educational grants from Philips Respironics and Dolby Vivisol, Research grants from Philips Respironics. SM: consultancy for Philips Respironics, educational grants from Dolby Vivisol. AS: educational grants from Dolby Vivisol.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence . Motor neurone disease: the use of non-invasive ventilation in the management of motor neurone disease. London: (NICE) NIfHaCE, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Muscular Dystrophy UK . Right to breathe: Access to respiratory care for people with a muscle-wasting conditions. London: Muscular Dystrophy UK, 2015.
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical