Strategies for labelling of exogenous and endogenous extracellular vesicles and their application for in vitro and in vivo functional studies
- PMID: 38461237
- PMCID: PMC10924393
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01548-3
Strategies for labelling of exogenous and endogenous extracellular vesicles and their application for in vitro and in vivo functional studies
Abstract
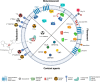
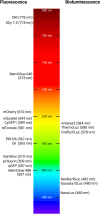
This review presents a comprehensive overview of labelling strategies for endogenous and exogenous extracellular vesicles, that can be utilised both in vitro and in vivo. It covers a broad spectrum of approaches, including fluorescent and bioluminescent labelling, and provides an analysis of their applications, strengths, and limitations. Furthermore, this article presents techniques that use radioactive tracers and contrast agents with the ability to track EVs both spatially and temporally. Emphasis is also placed on endogenous labelling mechanisms, represented by Cre-lox and CRISPR-Cas systems, which are powerful and flexible tools for real-time EV monitoring or tracking their fate in target cells. By summarizing the latest developments across these diverse labelling techniques, this review provides researchers with a reference to select the most appropriate labelling method for their EV based research.
Keywords: Bioluminescent labelling; CRISPR-Cas; Cre-loxP; EV tracking; Exosomes; Extracellular vesicles; Fluorescent labelling; In vivo imaging; Magnetic resonance; Radiolabelling.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

