Pegylated-liposomal Doxorubicin-induced Glomerular Thrombotic Microangiopathy
- PMID: 38462521
- PMCID: PMC11557202
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3113-23
Pegylated-liposomal Doxorubicin-induced Glomerular Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Abstract
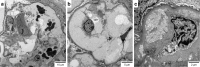
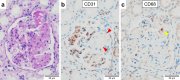
Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) has emerged as a recent innovation within the realm of antineoplastic agents, distinguished by its incorporation of doxorubicin within the liposomal bilayer. Given the low risk of cardiotoxicity, the clinical use of PLD has been expanding. We encountered a patient who underwent extended PLD therapy for recurrent malignancy and subsequently developed PLD-associated thrombotic microangiopathy, which was diagnosed by a detailed pathophysiological assessment. This case underscores the importance of considering thrombotic microangiopathy as a potential differential diagnosis in patients presenting with unexplained hypertension and renal impairment during prolonged PLD monotherapy.
Keywords: drug induced kidney injury; liposome; ovarian cancer; polyethylene glycol (PEG); proteinuria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin-induced renal toxicity in retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a case report and literature review.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021 Feb;87(2):289-294. doi: 10.1007/s00280-020-04203-z. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33388949 Review.
-
Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Causes Kidney-limited Thrombotic Microangiopathy.Am J Kidney Dis. 2024 Apr;83(4):549-553. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.08.014. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024. PMID: 37839689 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac safety profile of patients receiving high cumulative doses of pegylated-liposomal doxorubicin: use of left ventricular ejection fraction is of unproven value.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;80(4):787-798. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3420-8. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28856562
-
Selective cardiac surveillance in patients with gynecologic cancer undergoing treatment with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD).Gynecol Oncol. 2015 Jun;137(3):503-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.02.020. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Gynecol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25735254
-
Cardiac safety analysis of first-line chemotherapy drug pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2022 Aug 16;15(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-01029-6. J Ovarian Res. 2022. PMID: 35971131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Comprehensive Update.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 May 30;12(6):207. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12060207. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40558642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singal PK, Iliskovic N. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 339: 900-905, 1998. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien ME, Wigler N, Inbar M, et al. . Reduced cardiotoxicity and comparable efficacy in a phase III trial of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin HCl (CAELYX™/DoxilⓇ) versus conventional doxorubicin for first-line treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 15: 440-449, 2004. - PubMed
-
- George JN, Nester CM. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N Engl J Med 371: 654-666, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Genest DS, Patriquin CJ, Licht C, John R, Reich HN. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy: a review. Am J Kidney Dis 81: 591-605, 2023. - PubMed

