Prevalence and clinical characteristics of hyperuricemia among patients with chronic kidney disease under haemodialysis in a tertiary care center: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38463060
- PMCID: PMC10923382
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001731
Prevalence and clinical characteristics of hyperuricemia among patients with chronic kidney disease under haemodialysis in a tertiary care center: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Hyperuricemia is common in chronic kidney disease patients. This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and clinical characteristics of hyperuricemia in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing haemodialysis.
Materials and methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted among 104 patients with chronic kidney disease who visited the haemodialysis unit of a tertiary centre hospital from 11 September 2022, to 11 November 2022. A convenience sampling technique was used. The data were collected using a proforma form, entered into, and analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 21.
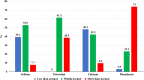
Results: The mean age group of the study participants was 54.02 ± 14.03 years, and around two-thirds were male (n=70, 67.3%). Almost half of the participants (50, 48.07%) had hyperuricemia with a mean uric acid level of 6.76 ± 2.62 mg/dl. The majority of the participants had associated hypertension (n=100, 96.2%). More than three-fourths of the respondents (83, 79.8%) had haemoglobin levels below the target range.
Conclusion: Nearly half of the study participants had hyperuricemia.
Keywords: Nepal; chronic renal insufficiency; cross-sectional study; hyperuricemia; renal dialysis.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
End Stage Renal Disease among Patients Undergoing Haemodialysis at a Tertiary Care Centre: A Descriptive Cross-sectional Study.JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2022 May 5;60(249):448-452. doi: 10.31729/jnma.7258. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35633246 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperuricemia and Progression of CKD in Children and Adolescents: The Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) Cohort Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Dec;66(6):984-92. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 26209544 Free PMC article.
-
Demographic and clinical profile of black patients with chronic kidney disease attending a tertiary hospital in Johannesburg, South Africa.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 19;17(9):e0266155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266155. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36121812 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperuricemia, the kidneys, and the spectrum of associated diseases: a narrative review.Curr Med Res Opin. 2016 Nov;32(11):1863-1869. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2016.1218840. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016. PMID: 27470664 Review.
-
Hyperuricemia and Hypertension, Coronary Artery Disease, Kidney Disease: From Concept to Practice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 6;21(11):4066. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114066. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33561034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- KDIGO 2012Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Off J Int Soc Nephrol, 3x. - PubMed
-
- Chuang SY, Chen JH, Yeh WT, et al. . Hyperuricemia and increased risk of ischemic heart disease in a large Chinese cohort. Int J Cardiol 2012;154:316–321. - PubMed
-
- Ohno I. Relationship between hyperuricemia and chronic kidney disease. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2011;30:1039–1044. - PubMed
-
- Barbour SJ, Er L, Djurdjev O, et al. . The prevalence of hematologic and metabolic abnormalities during chronic kidney disease stages in different ethnic groups. Kidney Int 2008;74:108–114. - PubMed
-
- Stack AG, Hanley A, Casserly LF, et al. . Independent and conjoint associations of gout and hyperuricaemia with total and cardiovascular mortality. QJM 2013;106:647–658. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources