Feasibility of using real-world free thyroxine data from the US and Europe to enable fast and efficient transfer of reference intervals from one population to another
- PMID: 38463194
- PMCID: PMC10924049
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plabm.2024.e00382
Feasibility of using real-world free thyroxine data from the US and Europe to enable fast and efficient transfer of reference intervals from one population to another
Abstract
Objectives: The direct approach for determining reference intervals (RIs) is not always practical. This study aimed to generate evidence that a real-world data (RWD) approach could be applied to transfer free thyroxine RIs determined in one population to a second population, presenting an alternative to performing multiple RI determinations.
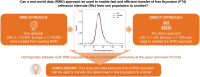
Design and methods: Two datasets (US, n = 10,000; Europe, n = 10,000) were created from existing RWD. Descriptive statistics, density plots and cumulative distributions were produced for each data set and comparisons made. Cumulative probabilities at the lower and upper limits of the RIs were identified using an empirical cumulative distribution function. According to these probabilities, estimated percentiles for each dataset and estimated differences between the two sets of percentiles were obtained by case resampling bootstrapping. The estimated differences were then evaluated against a pre-determined acceptance criterion of ≤7.8% (inter-individual biological variability). The direct approach was used to validate the RWD approach.
Results: The RWD approach provided similar descriptive statistics for both populations (mean: US = 16.1 pmol/L, Europe = 16.4 pmol/L; median: US = 15.4 pmol/L, Europe = 15.8 pmol/L). Differences between the estimated percentiles at the upper and lower limits of the RIs fulfilled the pre-determined acceptance criterion and the density plots and cumulative distributions demonstrated population homogeneity. Similar RI distributions were observed using the direct approach.
Conclusions: This study provides evidence that a RWD approach can be used to transfer RIs determined in one population to another.
Keywords: Direct approach; Free thyroxine; Indirect approach; Real-world data; Reference intervals.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Hedwig Kurka, Peter Dilba, Thorsten Rehberg, Benedikt Weber, Horst Donner and Anja Thorenz are employees of Roche Diagnostics GmbH. Alex Katayev and André Valcour are employees of Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings (Labcorp). Ignacio Gadea Gironés, Carlos Castillo Perez, Peter Findeisen and Laura Rodríguez Alonso have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Katayev A., Balciza C., Seccombe D.W. Establishing reference intervals for clinical laboratory test results: is there a better way? Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010;133(2):180–186. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz G.L., Altaie S., Boyd J.C., Ceriotti F., Garg U., Horn P., Pesce A., Sine H.E., Zakowski J. third ed. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute; Wayne, PA: 2016. Defining, Establishing, and Verifying Reference Intervals in the Clinical Laboratory; Approved Guideline.
-
- Horowitz G.L. Estimating reference intervals. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010;133(2):175–177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

