Aquaporin-5 Protein Is Selectively Reduced in Rat Parotid Glands under Conditions of Fasting or a Liquid Diet
- PMID: 38463206
- PMCID: PMC10918431
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.24-00003
Aquaporin-5 Protein Is Selectively Reduced in Rat Parotid Glands under Conditions of Fasting or a Liquid Diet
Abstract
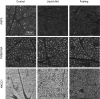
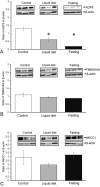
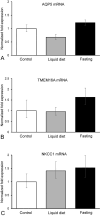
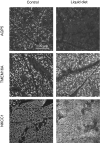
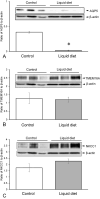
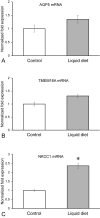
Aquaporin-5 (AQP5) water channel, transmembrane protein 16A (TMEM16A) Ca2+-activated Cl- channel, and Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter (NKCC1) are membrane proteins on salivary gland acinar cells that function in watery saliva secretion. We examined their expression changes in rat parotid glands under reduced mastication. Rats were either fed regular chow as a control group, fasted for 48 hr or fed a liquid diet for 48 hr or 1 week to reduce mastication. The parotid glands were then resected to analyze the protein and mRNA levels by immunofluorescence, immunoblotting, and reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). AQP5 protein was significantly decreased in both liquid diet groups and the fasting group but its mRNA levels showed no apparent changes compared with the control group. The protein and mRNA levels of TMEM16A and NKCC1 showed no significant changes between any of the groups other than an increase in NKCC1 mRNA in the 1-week liquid diet group. These results suggest that reduced mastication may increase the AQP5 protein degradation, but not that of other membrane proteins necessary for saliva secretion.
Keywords: AQP5; fasting; liquid diet; parotid gland.
2024 The Japan Society of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
VThe authors declare no competing financial or other interests in relation to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Azlina, A., Javkhlan, P., Hiroshima, Y., Hasegawa, T., Yao, C., Akamatsu, T., et al. (2010) Roles of lysosomal proteolytic systems in AQP5 degradation in the submandibular gland of rats following chorda tympani parasympathetic denervation. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 299; G1106–G1117. - PubMed
-
- Evans, R. L., Park, K., Turner, R. J., Watson, G. E., Nguyen, H. V., Dennett, M. R., et al. (2000) Severe impairment of salivation in Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter (NKCC1)-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 275; 26720–26726. - PubMed
-
- Hand, A. R. and Ball, W. D. (1988) Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of secretory proteins in autophagic vacuoles of parotid acinar cells of starved rats. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine 17; 279–286. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

