Formulation of Folate Receptor-Targeted Silibinin-Loaded Inhalable Chitosan Nanoparticles by the QbD Approach for Lung Cancer Targeted Delivery
- PMID: 38463259
- PMCID: PMC10918659
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07954
Formulation of Folate Receptor-Targeted Silibinin-Loaded Inhalable Chitosan Nanoparticles by the QbD Approach for Lung Cancer Targeted Delivery
Abstract
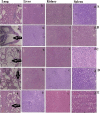
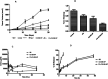
Aim: Targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics by functionalized nanoparticles exhibits a wonderful prospect for cancer treatment. The main objective of this research was to develop folate receptor-targeted silibinin (SB)-loaded inhalable polymeric nanoparticles (FA-CS-SB-NPs) for the treatment of lung cancer. Method: The qbD approach was implemented to prepare SB-loaded nanoparticles. Folic acid was conjugated by electrostatic conjugation in an optimized batch. The therapeutic potentials of formulations were determined using a lung cancer cell-bearing rat model. Result: Optimized formulation exhibited a spherical surface with a mean particle size of 275 ± 1.20 nm, a PDI of 0.234 ± 0.07, a ζ-potential of 32.50 ± 0.21, an entrapment efficiency of 75.52 ± 0.87%, and a CDR of 63.25 ± 1.21% at 48 h. Aerodynamic behaviors such as the mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) and geometric size distribution (GSD) were found to be 2.75 ± 1.02 and 3.15 ± 0.88 μm, respectively. After 24 h of incubation with FA-CS-SB-NPs, the IC50 value was found to be 24.5 g/mL. FA-SB-CS-NPs maintained a significantly higher deposition of SB in lung tissues. Conclusions: Thus, the noninvasive nature and target specificity of FA-CS-SB-NPs pave the way for pulmonary delivery for treating lung cancer.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



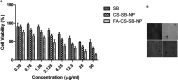

Similar articles
-
Silibinin loaded inhalable solid lipid nanoparticles for lung targeting.J Microencapsul. 2022 Jan;39(1):1-24. doi: 10.1080/02652048.2021.2002448. Epub 2021 Dec 6. J Microencapsul. 2022. PMID: 34825627
-
Lung cancer targeting efficiency of Silibinin loaded Poly Caprolactone /Pluronic F68 Inhalable nanoparticles: In vitro and In vivo study.PLoS One. 2022 May 13;17(5):e0267257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267257. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35560136 Free PMC article.
-
Building and behavior of a pH-stimuli responsive chitosan nanoparticles loaded with folic acid conjugated gemcitabine silver colloids in MDA-MB-453 metastatic breast cancer cell line and pharmacokinetics in rats.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Oct 1;165:105938. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2021.105938. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34256103
-
5-Fluorouracil-Loaded Folic-Acid-Fabricated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Site-Targeted Drug Delivery Cargo.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 13;14(10):2010. doi: 10.3390/polym14102010. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631891 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted delivery and apoptosis induction of CDK-4/6 inhibitor loaded folic acid decorated lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles in breast cancer cells.Int J Pharm. 2024 Feb 15;651:123787. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.123787. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38184023
Cited by
-
Lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles against lung cancer and their application as inhalable formulation.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024;19(25):2113-2133. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2387530. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39143915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in controlled release drug delivery systems based on nanomaterials in lung cancer therapy: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 7;104(6):e41415. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041415. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39928802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Silibinin Combined With EGFR-TKIs in the Treatment of NSCLC.Cancer Med. 2025 Feb;14(3):e70643. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70643. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39907159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang J.; Liu Y. M.; Liu Y. Z. Advances in the pharmaceutical research on the silymarin. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2004, 16 (2), 185–187.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
