Carbon Dot Based Carbon Nanoparticles as Potent Antimicrobial, Antiviral, and Anticancer Agents
- PMID: 38463310
- PMCID: PMC10918813
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05537
Carbon Dot Based Carbon Nanoparticles as Potent Antimicrobial, Antiviral, and Anticancer Agents
Abstract
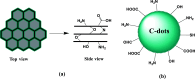
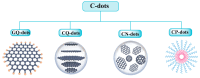
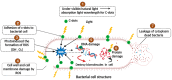
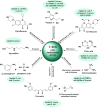
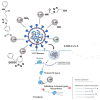
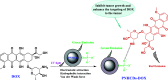
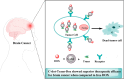
Antimicrobial and anticancer drugs are widely used due to increasing widespread infectious diseases caused by microorganisms such as bacterial, fungal, viral agents, or cancer cells, which are one of the major causes of mortality globally. Nevertheless, several microorganisms developed resistance to antibiotics as a result of genetic changes that have occurred over an extended period. Carbon-based materials, particularly carbon dots (C-dots), are potential candidates for antibacterial and anticancer nanomaterials due to their low toxicity, ease of synthesis and functionalization, high dispersibility in aqueous conditions, and promising biocompatibility. In this Review, the content is divided into four sections. The first section concentrates on C-dot structures, surface functionalization, and morphology. Following that, we summarize C-dot classifications and preparation methods such as arc discharge, laser ablation, electrochemical oxidation, and so on. The antimicrobial applications of C-dots as antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral agents both in vivo and in vitro are discussed. Finally, we thoroughly examined the anticancer activity displayed by C-dots.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Graphene oxide and carbon dots as broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents - a minireview.Nanoscale Horiz. 2019 Jan 1;4(1):117-137. doi: 10.1039/c8nh00174j. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019. PMID: 32254148 Review.
-
Carbon Dots for Killing Microorganisms: An Update since 2019.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;15(10):1236. doi: 10.3390/ph15101236. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon Dots for Bacterial Detection and Antibacterial Applications-A Minireview.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(46):4848-4860. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191216150948. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31840599 Review.
-
Carbon Quantum Dots: Properties, Preparation, and Applications.Molecules. 2024 Apr 26;29(9):2002. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092002. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon Dots as Drug Delivery Vehicles for Antimicrobial Applications: A Minireview.ChemMedChem. 2022 Jul 5;17(13):e202200003. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202200003. Epub 2022 May 27. ChemMedChem. 2022. PMID: 35429414 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced antiviral defense against begomoviral infection in Nicotiana benthamiana through strategic utilization of fluorescent carbon quantum dots to activate plant immunity.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Nov 14;22(1):707. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02994-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39543670 Free PMC article.
-
Photoactivated carbon dots immobilized on cellulose for antibacterial activity and biofilm inhibition.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 25;15(1):27020. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12317-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40707616 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles Loaded with Pralidoxime Wrapped in Tumor Cell Membranes: A New Strategy to Counteract the Central Nervous System Effects of Organophosphate Poisoning.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 24;20:8101-8118. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S516233. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40584778 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Antimicrobial and Biofilm-Disrupting Properties of Gallium-Doped Carbon Dots.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 20;10(25):27559-27574. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03575. eCollection 2025 Jul 1. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40621032 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Interactions with the Blood Brain Barrier: Insights from Drosophila and Implications for Human Astrocyte Targeted Therapies.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jan 20;50(1):80. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04333-x. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 39832031 Review.
References
-
- Sun Y.-P.; Zhou B.; Lin Y.; Wang W.; Fernando K. A. S.; Pathak P.; Meziani M. J.; Harruff B. A.; Wang X.; Wang H.; Luo P. G.; Yang H.; Kose M. E.; Chen B.; Veca L. M.; Xie S.-Y.; et al. Quantum-Sized Carbon Dots for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128 (24), 7756–7757. 10.1021/ja062677d. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roy P.; Chen P. C.; Periasamy A. P.; Chen Y. N.; Chang H. T. Photoluminescent carbon nanodots: synthesis, physicochemical properties and analytical applications. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 44710.1016/j.mattod.2015.04.005. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
