Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Synthetic Biology: Key Architectures, Applications, and Challenges
- PMID: 38463314
- PMCID: PMC10918679
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05913
Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Synthetic Biology: Key Architectures, Applications, and Challenges
Abstract
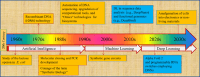
Machine learning (ML), particularly deep learning (DL), has made rapid and substantial progress in synthetic biology in recent years. Biotechnological applications of biosystems, including pathways, enzymes, and whole cells, are being probed frequently with time. The intricacy and interconnectedness of biosystems make it challenging to design them with the desired properties. ML and DL have a synergy with synthetic biology. Synthetic biology can be employed to produce large data sets for training models (for instance, by utilizing DNA synthesis), and ML/DL models can be employed to inform design (for example, by generating new parts or advising unrivaled experiments to perform). This potential has recently been brought to light by research at the intersection of engineering biology and ML/DL through achievements like the design of novel biological components, best experimental design, automated analysis of microscopy data, protein structure prediction, and biomolecular implementations of ANNs (Artificial Neural Networks). I have divided this review into three sections. In the first section, I describe predictive potential and basics of ML along with myriad applications in synthetic biology, especially in engineering cells, activity of proteins, and metabolic pathways. In the second section, I describe fundamental DL architectures and their applications in synthetic biology. Finally, I describe different challenges causing hurdles in the progress of ML/DL and synthetic biology along with their solutions.
© 2024 The Author. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Concepts and Applications for Synthetic Biology.GEN Biotechnol. 2022 Aug 1;1(4):360-371. doi: 10.1089/genbio.2022.0017. Epub 2022 Aug 18. GEN Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36061221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosystems Design by Machine Learning.ACS Synth Biol. 2020 Jul 17;9(7):1514-1533. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00129. Epub 2020 Jun 29. ACS Synth Biol. 2020. PMID: 32485108 Review.
-
Synthetic Biology Meets Machine Learning.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2553:21-39. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2617-7_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36227537
-
Application of Meta-Heuristic Algorithms for Training Neural Networks and Deep Learning Architectures: A Comprehensive Review.Neural Process Lett. 2022 Oct 31:1-104. doi: 10.1007/s11063-022-11055-6. Online ahead of print. Neural Process Lett. 2022. PMID: 36339645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning in Hematology: From Molecules to Patients.Clin Hematol Int. 2024 Oct 8;6(4):19-42. doi: 10.46989/001c.124131. eCollection 2024. Clin Hematol Int. 2024. PMID: 39417017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Predictive Accuracy for Recurrence-Free Survival in Head and Neck Tumor: A Comparative Study of Weighted Fusion Radiomic Analysis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;14(18):2038. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14182038. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335718 Free PMC article.
-
Design of fully synthetic signal peptide library and its use for enhanced secretory production of recombinant proteins in Corynebacterium glutamicum.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Sep 16;23(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02516-9. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39285401 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of genomic biomarkers for endometriosis using the transcriptomic dataset.World J Clin Cases. 2025 Jul 16;13(20):104556. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i20.104556. World J Clin Cases. 2025. PMID: 40671745 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling DNA engineering.Trends Biotechnol. 2025 May 28:S0167-7799(25)00168-4. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2025.05.002. Online ahead of print. Trends Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40441920 Review.
-
Biosynthesis Strategies and Application Progress of Mandelic Acid Based on Biomechanical Properties.Microorganisms. 2025 Jul 23;13(8):1722. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13081722. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40871226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jumper J.; Evans R.; Pritzel A.; Green T.; Figurnov M.; Ronneberger O.; Tunyasuvunakool K.; Bates R.; Žídek A.; Potapenko A.; Bridgland A.; Meyer C.; Kohl S. A. A.; Ballard A. J.; Cowie A.; Romera-Paredes B.; Nikolov S.; Jain R.; Adler J.; Back T.; Petersen S.; Reiman D.; Clancy E.; Zielinski M.; Steinegger M.; Pacholska M.; Berghammer T.; Bodenstein S.; Silver D.; Vinyals O.; Senior A. W.; Kavukcuoglu K.; Kohli P.; Hassabis D. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. 10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
