Early endoscopic management of an infected acute necrotic collection misdiagnosed as a pancreatic pseudocyst: A case report
- PMID: 38463375
- PMCID: PMC10921193
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.609
Early endoscopic management of an infected acute necrotic collection misdiagnosed as a pancreatic pseudocyst: A case report
Abstract
Background: Infected acute necrotic collection (ANC) is a fatal complication of acute pancreatitis with substantial morbidity and mortality. Drainage plays an exceedingly important role as the first step in invasive intervention for infected necrosis; however, there is great controversy about the optimal drainage time, and better treatment should be explored.
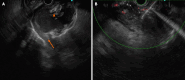
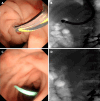
Case summary: We report the case of a 43-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital with severe intake reduction due to early satiety 2 wk after treatment for acute pancreatitis; conservative treatment was ineffective, and a pancreatic pseudocyst was suspected on contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT). Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) suggested hyperechoic necrotic tissue within the cyst cavity. The wall was not completely mature, and the culture of the puncture fluid was positive for A-haemolytic Streptococcus. Thus, the final diagnosis of ANC infection was made. The necrotic collection was not walled off and contained many solid components; therefore, the patient underwent EUS-guided aspiration and lavage. Two weeks after the collection was completely encapsulated, pancreatic duct stent drainage via endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was performed, and the patient was subsequently successfully discharged. On repeat CT, the pancreatic cysts had almost disappeared during the 6-month follow-up period after surgery.
Conclusion: Early EUS-guided aspiration and lavage combined with late ERCP catheter drainage may be effective methods for intervention in infected ANCs.
Keywords: Case report; Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; Endoscopic ultrasonography; Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration; Infected acute necrotic collection; Pancreatic pseudocyst.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage for spontaneous rupture of a pancreatic pseudocyst into the peritoneal cavity in a patient with autoimmune pancreatitis.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug;13(4):591-596. doi: 10.1007/s12328-020-01104-9. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32078121
-
American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Update: Management of Pancreatic Necrosis.Gastroenterology. 2020 Jan;158(1):67-75.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.064. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 31479658 Review.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic fluid collections' transmural drainage outcomes in 100 consecutive cases of pseudocysts and walled off necrosis: a single-centre experience from the United Kingdom.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018 May;53(5):611-615. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2017.1398346. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29117722
-
Pseudocyst in the pancreatic tail associated with chronic pancreatitis successfully treated by transpapillary cyst drainage.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2008 Sep;2(3):390-7. doi: 10.1159/000163377. Epub 2008 Nov 11. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 21897788 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic pseudocyst-portal vein fistula: a case treated with EUS-guided cyst-drainage and a review of the literature.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug;13(4):597-606. doi: 10.1007/s12328-020-01105-8. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32215857 Review.
References
-
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee. Muthusamy VR, Chandrasekhara V, Acosta RD, Bruining DH, Chathadi KV, Eloubeidi MA, Faulx AL, Fonkalsrud L, Gurudu SR, Khashab MA, Kothari S, Lightdale JR, Pasha SF, Saltzman JR, Shaukat A, Wang A, Yang J, Cash BD, DeWitt JM. The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory pancreatic fluid collections. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:481–488. - PubMed
-
- Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG, Vege SS Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Chahal P, Baron TH, Topazian MD, Levy MJ. EUS-guided diagnosis and successful endoscopic transpapillary management of an intrahepatic pancreatic pseudocyst masquerading as a metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma (with videos) Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:393–396. - PubMed
-
- Trikudanathan G, Wolbrink DRJ, van Santvoort HC, Mallery S, Freeman M, Besselink MG. Current Concepts in Severe Acute and Necrotizing Pancreatitis: An Evidence-Based Approach. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1994–2007.e3. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

