Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38463530
- PMCID: PMC10921441
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2023-0874
Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
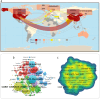
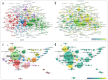
Advances in lung cancer research applying machine learning (ML) technology have generated many relevant literature. However, there is absence of bibliometric analysis review that aids a comprehensive understanding of this field and its progress. Present article for the first time performed a bibliometric analysis to clarify research status and focus from 2010 to 2021. In the analysis, a total of 2,312 relevant literature were searched and retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection database. We conducted a bibliometric analysis and further visualization. During that time, exponentially growing annual publication and our model have shown a flourishing research prospect. Annual citation reached the peak in 2017. Researchers from United States and China have produced most of the relevant literature and strongest partnership between them. Medical image analysis and Nature appeared to bring more attention to the public. The computer-aided diagnosis, precision medicine, and survival prediction were the focus of research, reflecting the development trend at that period. ML did make a big difference in lung cancer research in the past decade.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; burstiness; collaboration; global trend; lung cancer; machine learning.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflict to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF, Heist RS. Lung cancer. Lancet. 2021;398(10299):535–54. - PubMed
-
- Fillon M. Pairing smoking cessation with lung cancer screening may save lives. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(4):283–4. - PubMed
-
- Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(8):1623–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
