Expression of circular RNA has-circ-0009158 and identification of associated miRNA-mRNA network in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38463586
- PMCID: PMC10918124
- DOI: 10.62347/MYMM7384
Expression of circular RNA has-circ-0009158 and identification of associated miRNA-mRNA network in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
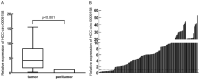
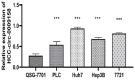
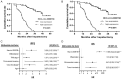
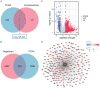
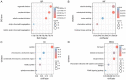
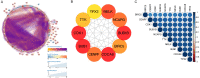
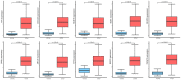
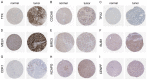
Primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) affects people all over the world. Circular RNAs are involved in the growth and development of several malignancies and regulate a number of biological processes. However, the roles of has-circ-0009158 in HCC remain unknown. This study explored the expression and associated miRNA-mRNA network of has-circ-0009158 in HCC. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to measure the expression of hsa-circ-0009158 in the HCC tissues of 143 patients and four human HCC cell lines. Then, the potential relationship of hsa-circ-0009158 expression with clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients was analyzed using the GO and KEGG databases. Correlated miRNA-mRNA networks were forecasted using the TCGA database and Cytoscape software. The hsa-circ-0009158 expression was significantly upregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines (P<0.001). The multivariate Cox analysis revealed that HCC patients were associated with high hsa-circ-0009158 expression. The bioinformatics analysis screened 1 miRNA, and 248 mRNAs associated with the circRNA in HCC. A pathway analysis suggested that the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) may be linked to the development and growth of HCC tumors. Ten hub genes (MELK, NCAPG, BUB1B, BIRC5, CDCA8, CENPF, BUB1, CDK1, TTK, TPX2) were identified from the PPI network based on the 248 genes. Additionally, the 10 hub genes that were verified had an association between high expression levels and low overall survival rates. As a result, the high expression of hsa-circ-0009158 was found to be a separate risk factor for recurrence and a poor prognosis in HCC patients.
Keywords: Circular RNA; hepatocellular carcinoma; hsa-circ-0009158; poor prognosis; recurrence.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Lencioni R, Koike K, Zucman-Rossi J, Finn RS. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:6. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidencebased diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:835–853. - PubMed
-
- Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer M, Loewer A, Ziebold U, Landthaler M, Kocks C, le Noble F, Rajewsky N. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495:333–338. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
