Effects of Shixiao Huoxue Decoction on pain, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-8 in patients with adenomyosis
- PMID: 38463587
- PMCID: PMC10918143
- DOI: 10.62347/VQVR4400
Effects of Shixiao Huoxue Decoction on pain, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-8 in patients with adenomyosis
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of Shixiao Huoxue Decoction on pain and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-8 levels in patients with adenomyosis.
Methods: A total of 65 patients with adenomyosis admitted to South District of Guang'anmen Hospital from January 2020 to December 2021 were divided into two groups according to the treatment methods. The control group was treated with pregnatrienone, and the study group was treated with additional Shixiaohuoxue decoction. The incidence of complications, treatment efficacy, levels of inflammatory factors, Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom score, dysmenorrhea score, menstrual volume score, dysmenorrhea symptom score, changes in uterine volume, level of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and changes in the level of carbohydrate antigen (CA125) were observed before and after treatment in both two groups. Univariate Logistic analysis showed that uterine volume, IGF-1, CA125, serum IL-8 and TNF-α were correlated with the short-term efficacy of Meixiaohuoxue Decoction in the treatment of uterine adenomyosis (P<0.05).
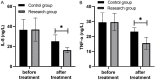
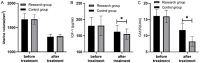
Results: The levels of IL-8 and TNF-α in the study group were significantly lower than those in the control group after treatment (P<0.05). The scores of dyspareunia and non-menstrual pelvic pain in the study group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). The overall response rate in the study group (93.75%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (66.66%) (P<0.05). The scores of Traditional Chinese Medicine symptoms, dysmenorrhea, menstrual volume, and dysmenorrhea symptoms in the study group were significantly lower than those in the control group after treatment (P<0.05). The IGF-1 and CA125 levels in the study group were significantly lower than those in the control group after treatment (P<0.05). However, no significant difference in uterine volume was found between the two groups after treatment (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Xiaoxiao Huoxue Decoction demonstrated a better treatment efficacy in patients with adenomyosis through improving dysmenorrhea and Traditional Chinese Medicine symptoms, as well as reducing the levels of body inflammatory factors, non-menstrual pelvic pain, and dyspareunia, thus contributing to early recovery of patients. Therefore, Xiaoxiao Huoxue Decoction is worthy of promotion in clinical treatment of adenomyosis.
Keywords: Xiaoxiao Huoxue Decoction; adenomyosis; interleukin-8; pain; tumor necrosis factor-α.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Treatment of adenomyosis patients by bushen huoxue sanyu decoction: a clinical study].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014 Nov;34(11):1302-5. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25566618 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonist combined with high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for adenomyosis: a clinical study.BJOG. 2017 Aug;124 Suppl 3:7-11. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14736. BJOG. 2017. PMID: 28856862
-
[Evaluation of the efficacy of GnRH-a pretreatment before total hysterectomy for adenomyosis patients: a propensity score matching analysis].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Aug 25;58(8):589-594. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20230607-00257. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37599256 Chinese.
-
Efficacy of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Combined With GnRH-a for Adenomyosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2021 Aug 16;9:688264. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.688264. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34485218 Free PMC article.
-
The Outcome of Fertility-Sparing and Nonfertility-Sparing Surgery for the Treatment of Adenomyosis. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 Feb;27(2):309-331.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2019.08.004. Epub 2019 Aug 6. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 31398415
Cited by
-
Research Advances in Adenomyosis-Related Signaling Pathways and Promising Targets.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 4;14(11):1402. doi: 10.3390/biom14111402. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39595579 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hassanin AI, Youssef AA, Yousef AM, Ali MK. Comparison of dienogest versus combined oral contraceptive pills in the treatment of women with adenomyosis: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2021;154:263–269. - PubMed
-
- Hou X, Xing J, Shan H, Mei J, Sun Y, Yan G, Sun H, Wang J. The effect of adenomyosis on IVF after long or ultra-long GnRH agonist treatment. Reprod Biomed Online. 2020;41:845–853. - PubMed
-
- Crha Karel, Ješeta Michal, Pilka Radovan, Ventruba Pavel, Žáková Jana, Vodička Jan, Crha Tomáš. Adenomyosis - its possible effect on endometrial function and receptivity. Ceska Gynekol. 2021;86:205–209. - PubMed
-
- Kim MS, Jang JH, Park S, Ahn EH, Jung SH. Effect of adenomyosis on adverse obstetrical outcomes in twin pregnancies achieved with assisted reproductive technology. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2021;41:1225–1229. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Wang K, Di A, Yu D, Yao T. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of adenomyosis: a narrative review. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10:12003–12011. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
