Efficacy comparison between acupuncture and other modalities in the treatment of rotator cuff diseases: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38463603
- PMCID: PMC10918137
- DOI: 10.62347/NCRJ1270
Efficacy comparison between acupuncture and other modalities in the treatment of rotator cuff diseases: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to analyze the efficacy of acupuncture alone or combined with physical therapy compared to other treatment interventions for relieving pain and improving function in rotator cuff diseases.
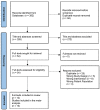
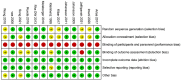
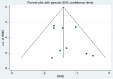
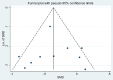
Methods: Our study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. After PROSPERO (CRD42023396740) registration, all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from the inception of the databases to October 10, 2023, evaluating the efficacy of acupuncture either alone or in combination with physical therapy for treating rotator cuff diseases, were extracted from seven databases, including PubMed, Embase, the Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), the VIP Database for Chinese Technical Periodicals (VIP), and the Wanfang Date. Two independent researchers assessed the quality of the included studies and extracted relevant data. Furthermore, a meta-analysis was conducted using Stata 14 software.
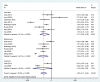
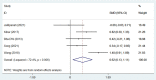
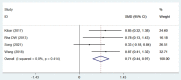
Results: We included 13 RCTs - 12 published in English and 1 in Chinese - that enrolled 1,371 patients. The meta-analysis results demonstrated that acupuncture alone or in combination with physical therapy was superior to other interventions for short-term shoulder joint function improvement (standardized mean difference [SMD] = -0.82, 95% confidence interval [95% CI]: -1.28 to -0.35, P = 0.001), medium-term shoulder joint function improvement (SMD = -1.00, 95% CI: -1.62 to -0.38, P = 0.002), short-term pain relief (weighted mean difference [WMD] = -1.37, 95% CI: -2.39 to -0.38, P = 0.006), medium-term pain relief (WMD = -1.66, 95% CI: -2.70 to -0.63, P = 0.002), and post-treatment shoulder joint abduction improvements (SMD = 0.68, 95% CI: 0.20 to 1.16, P = 0.005), external rotation (SMD = 0.62, 95% CI: 0.13 to 1.11, P = 0.012), and forward flexion (SMD = 0.71, 95% CI: 0.44 to 0.97, P < 0.001), with significant differences (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Based on the current clinical data, meta-analysis showed that acupuncture alone or combined with physical therapy is efficacious for short- and medium-term (< 3 months) pain relief and functional improvements. However, compared to other interventions, the efficacy of the long-term (3 to 12 months) period did not significantly differ. After treatment, these modalities displayed advantages such as improved shoulder joint abduction, external rotation, and forward flexion movements. However, no significant difference was noted in internal rotation movement. Thus, future studies might further investigate whether different acupuncture methods affect the efficacy of treating rotator cuff diseases and improving long-term outcome.
Keywords: Acupuncture; meta-analysis; physical therapy; rotator cuff diseases; rotator cuff injury; subacromial pain syndrome.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Greenberg DL. Evaluation and treatment of shoulder pain. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98:487–504. - PubMed
-
- Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yasar E, Yazicioglu K. Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:2609–2616. - PubMed
-
- Nourissat G, Ornetti P, Berenbaum F, Sellam J, Richette P, Chevalier X. Does platelet-rich plasma deserve a role in the treatment of tendinopathy? Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82:230–234. - PubMed
-
- Jo CH, Shin WH, Park JW, Shin JS, Kim JE. Degree of tendon degeneration and stage of rotator cuff disease. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25:2100–2108. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
