Sendai virus is robust and consistent in delivering genes into human pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 38463758
- PMCID: PMC10923719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27221
Sendai virus is robust and consistent in delivering genes into human pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
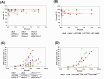
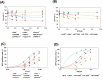
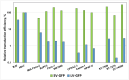
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly intratumorally heterogeneous disease that includes several subtypes and is highly plastic. Effective gene delivery to all PDAC cells is essential for modulating gene expression and identifying potential gene-based therapeutic targets in PDAC. Most current gene delivery systems for pancreatic cells are optimized for islet or acinar cells. Lentiviral vectors are the current main gene delivery vectors for PDAC, but their transduction efficiencies vary depending on pancreatic cell type, and are especially poor for the classical subtype of PDAC cells from both primary tumors and cell lines.
Methods: We systemically compare transduction efficiencies of glycoprotein G of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV-G)-pseudotyped lentiviral and Sendai viral vectors in human normal pancreatic ductal and PDAC cells.
Results: We find that the Sendai viral vector gives the most robust gene delivery efficiency regardless of PDAC cell type. Therefore, we propose using Sendai viral vectors to transduce ectopic genes into PDAC cells.
Keywords: Gene delivery; Pancreatic cancer; Sendai virus (SeV).
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Dual-Pseudotyped Lentiviral Vector with VSV-G and Sendai Virus HN Enhances Infection Efficiency through the Synergistic Effect of the Envelope Proteins.Viruses. 2024 May 23;16(6):827. doi: 10.3390/v16060827. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932120 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Evolution Generates Novel Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses with Improved Replication in Virus-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells.J Virol. 2020 Jan 17;94(3):e01643-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01643-19. Print 2020 Jan 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31694943 Free PMC article.
-
Intertumoral heterogeneity impacts oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus efficacy in mouse pancreatic cancer cells.J Virol. 2023 Sep 28;97(9):e0100523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01005-23. Epub 2023 Sep 6. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37671865 Free PMC article.
-
Lentiviral Vector Pseudotypes: Precious Tools to Improve Gene Modification of Hematopoietic Cells for Research and Gene Therapy.Viruses. 2020 Sep 11;12(9):1016. doi: 10.3390/v12091016. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32933033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding the Spectrum of Pancreatic Cancers Responsive to Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Oncolytic Virotherapy: Challenges and Solutions.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1171. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051171. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small Biological Fighters Against Cancer: Viruses, Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Protozoa, and Microalgae.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 8;13(3):665. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030665. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

