Ectopic Olfactory Neuroblastoma: Systematic Review of a Rare Clinical Entity among Sinonasal Tumors
- PMID: 38463937
- PMCID: PMC10923629
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1993-7790
Ectopic Olfactory Neuroblastoma: Systematic Review of a Rare Clinical Entity among Sinonasal Tumors
Abstract
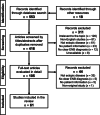
Objectives Ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma is an uncommon manifestation of an already rare neoplasm. We aimed to systematically review the literature for cases of ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma to better characterize this rare disease entity and to present two new case reports. Methods A search of the PubMed and Embase databases was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines to identify English-language articles reporting cases of ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma, published from 1955 through November 2021. Results Sixty-six cases of ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma were identified in 62 articles including the current review. Ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma arose in a wide age range (2-89 years) without significant sex predilection. It occurred most commonly in the ethmoid (25%), maxillary (25%), and sphenoid (16%) sinuses. Seventy-three percent of cases presented with low Hyams grade (I and II). The most common symptoms were nasal obstruction (32%) and epistaxis (32%). Paraneoplastic syndromes were observed in 27% of patients. The most common treatment was surgical resection followed by adjuvant radiotherapy. Overall, 76% of all patients were disease-free at the time of last follow-up. Locoregional recurrences and distant metastases were found in 19 and 5% of cases, respectively. Conclusion This systematic review describes previously reported cases of ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma, a disease entity with poorly understood characteristics. Physicians should consider olfactory neuroblastoma in the differential diagnosis for sinonasal masses, as their ectopic presentation may present considerable diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties. Patients with olfactory neuroblastoma may benefit from long-term follow-up and routine endoscopic examinations for surveillance of ectopic recurrences.
Keywords: ectopic; esthesioneuroblastoma; olfactory neuroblastoma; olfactory neuroepithelium; paraneoplastic syndrome; sinonasal tumor; systematic review.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma is associated with increased frequency of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion and reduced disease control: Case series with systematic review and pooled analysis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025 Jan;15(1):45-67. doi: 10.1002/alr.23502. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025. PMID: 39661032 Free PMC article.
-
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Release Secondary to Ectopic Olfactory Neuroblastoma: Case Report and Review of Literature.Ear Nose Throat J. 2023 Sep 30:1455613231199696. doi: 10.1177/01455613231199696. Online ahead of print. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023. PMID: 37776288
-
An atypical Esthesioneuroblastoma of the sphenoid sinus: a case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Apr 11;85(5):2029-2033. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000532. eCollection 2023 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37228980 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic primary olfactory neuroblastoma of the maxillary sinus.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2016 Jun;22:45-8. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27180059 Review.
-
Bilateral Synchronous Ectopic Ethmoid Sinus Olfactory Neuroblastoma: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2016 Apr 21;17:268-73. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.897623. Am J Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27097989 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma is associated with increased frequency of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion and reduced disease control: Case series with systematic review and pooled analysis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025 Jan;15(1):45-67. doi: 10.1002/alr.23502. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025. PMID: 39661032 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic surgery versus various open approaches in esthesioneuroblastoma: a systematic review of the literature.Front Oncol. 2025 May 28;15:1512771. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1512771. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40502638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger L, Luc R, Richard D. L'esthesioneuroepitheliome olfactif. Bull Assoc Fr Etud Cancer. 1924;13:410–421.
-
- Wormald R, Lennon P, O'Dwyer T P. Ectopic olfactory neuroblastoma: report of four cases and a review of the literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;268(04):555–560. - PubMed
-
- Dulguerov P, Allal A S, Calcaterra T C. Esthesioneuroblastoma: a meta-analysis and review. Lancet Oncol. 2001;2(11):683–690. - PubMed
-
- Broich G, Pagliari A, Ottaviani F.Esthesioneuroblastoma: a general review of the cases published since the discovery of the tumour in 1924 Anticancer Res 199717(4A):2683–2706. - PubMed